Figure 3.
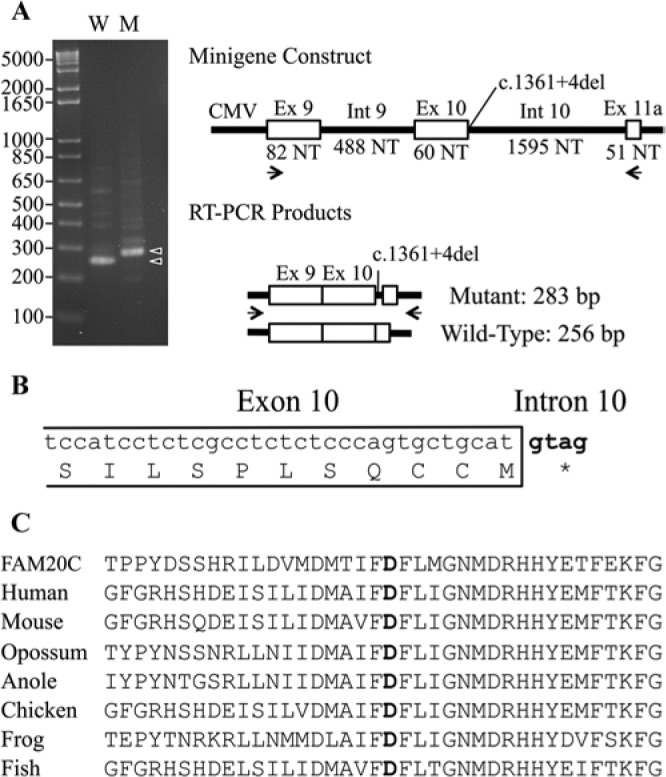
Analysis of disease-causing mutations. (A) Ethidium-bromide-stained agarose gel showing RT-PCR amplification products from the wild-type (W) and mutant (M) minigene constructs. The major amplification products (arrowheads) were 283 and 256 basepairs (bp) and differed by the inclusion of 27 bp from the 5′ end of Intron 10 in the mutated transcript. (B) Diagram showing the 3′ end of Exon 10 and how the extension of this exon into Intron 10 introduces an immediate stop codon that terminates translation after Met454. (C) Alignment of the human FAM20C amino acid sequence with FAM20A protein sequences from human (Homo sapiens), mouse (Mus musculus), opossum (Monodelphis domestica), anole (Anolis carolinensis), chicken (Gallus gallus), frog (Xenopus tropicalis), and fish (Danio rerio). The aspartic acid changed to asparagine in Family 1 is in bold.
