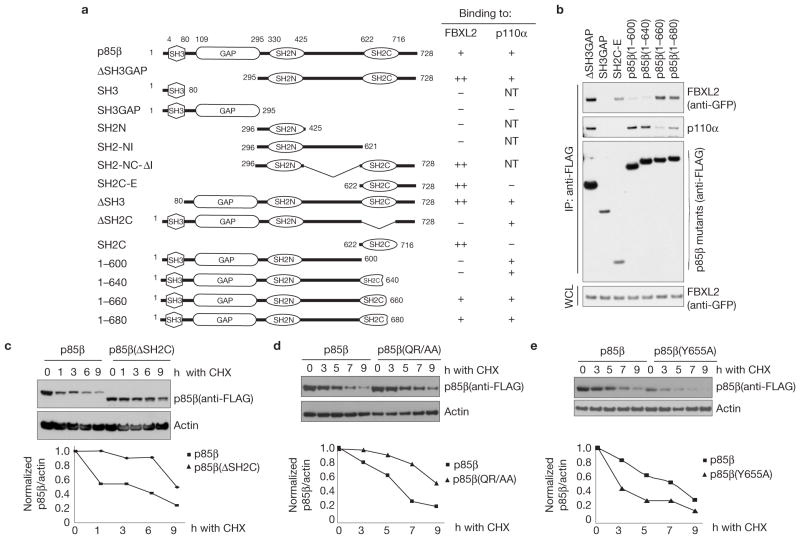
Figure 3.
Identification of p85β degron. (a) Schematic representation of p85β mutants. Binding of p85β to FBXL2 and p110α is indicated with the symbol +; NT, not tested. ‘++’ denotes enhanced binding. (b) HEK293T cells were transfected with GFP-tagged FBXL2 and the indicated FLAG-tagged p85β mutants. Whole-cell lysates (WCL) were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG resin, and immunocomplexes were probed with antibodies against the indicated proteins. (c) p85β(ΔSH2C) is more stable than wild-type p85β. RPE1-hTERT cells were infected with either a retrovirus expressing wild-type p85β or p85β (ΔSH2C). Cells were incubated with cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times, collected and analysed by immunoblotting as indicated. In the graph, the amount of p85β (wild-type or mutant) is represented relative to the amount at time 0. (d) p85β (QR/AA) is more stable than wild-type p85β. HEK293T cells were infected with either a retrovirus expressing wild-type p85β or p85β (QR/AA). Cells were incubated with cycloheximide (CHX) for the indicated times, collected and analysed by immunoblotting as indicated. In the graph, the amount of p85β (wild-type or mutant) is represented relative to the amount at time 0. (e) p85β (Y655A) is less stable than wild-type p85β. The experiment was performed as described in c except that p85β(Y655A) was used. In the graph, the amount of p85β(wild-type or mutant) is represented relative to the amount at time 0. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. S8.