Figure 1. PK-THPP and A1899 are potent rTASK-3 potassium channel antagonists.
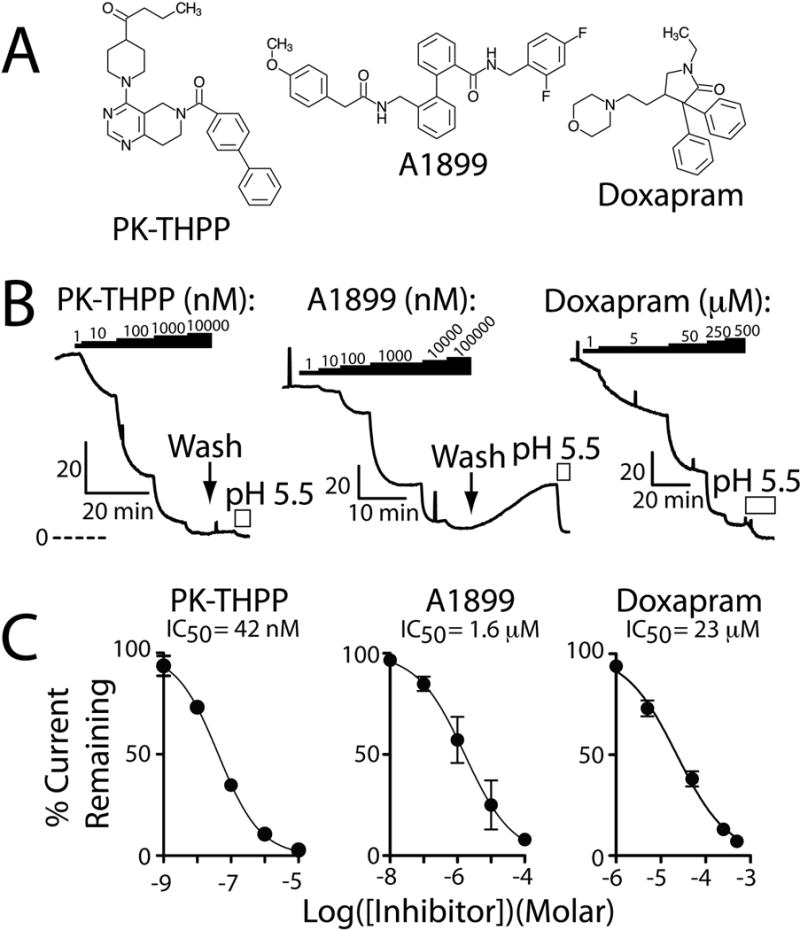
A, chemical structure of PK-THPP, A1899, and doxapram. B, Ussing chamber current records from FRT monolayers transiently expressing rTASK-3 and treated with PK-THPP, A1899, or doxapram. The black bars denote application of PK-THPP, A1899, or doxapram and the white bars indicate apical application of acidic pH. The perforated line indicates the zero current level, and the “L shaped” bars indicate current (μA/cm2) and time scaling. C, summary concentration-response data for PK-THPP, A1899, and doxapram. Each data point is n = 6 ± S.E.M.; error bars are not visible when smaller than data point. Data were fit with the following: I=100/(1+10ˆ((LogIC50−X)*HillSlope))). Hill Slope estimates were: PK-THPP −0.6953, A1899 −0.6124, and doxapram −0.7575.
