Table 1.
Effect of co-adsorbate on E-DNA signaling, specificity and reusability.
| Thiol | Chemical formula | Initial signal/μAa | (Itarget/Ibuffer)/% T-17b | (Itarget/Ibuffer)/% T-27b | (Itarget/Ibuffer)/% M-17b | Specificity ratio Rsc | Regeneration (Ireg/Ibuffer)/%d | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-mercaptoethanol |
|
3.9±0.3 | 62±3 | 70±4 | 50±3 | 1.2 | 85±5 | |
| 6-mercaptohexanol |
|
4.7±0.5 | 71±4 | 80±3 | 55±3 | 1.3 | 98±6 | |
| 11-mercaptoundecanol |
|
4.5±0.4 | 47±3 | 60±4 | 25±2 | 1.9 | 96±8 | |
| Cysteamine (2-mercaptoethylamine) |
|
5.9±0.7 | 90±6 d | 90±4 | 77±5 | 1.1 | 89±6 | |
| Mercaptoethane sulfonic acid |
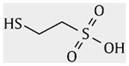
|
2.6±0.4 | 80±5 | 52±3 | 36±6 | 2.2 | 91±7 |
Signal in the presence of buffer.
% values of signal suppression (ratio of current signal obtained in target–Itarget–and current signal obtained in buffer -Ibuffer) as a result of target hybridization are the average and standard deviation of measurements performed with four independent sensors.
Rs is the ratio of the signal suppression (Itarget/Ibuffer) obtained with the fully complementary target (T-17) to that observed with the mismatched target (M-17).
% values of regeneration (ratio of current signal obtained in buffer after regeneration–Ireg–and current signal obtained in buffer–Ibuffer) are the average and standard deviation of measurements performed with four independent sensors.
