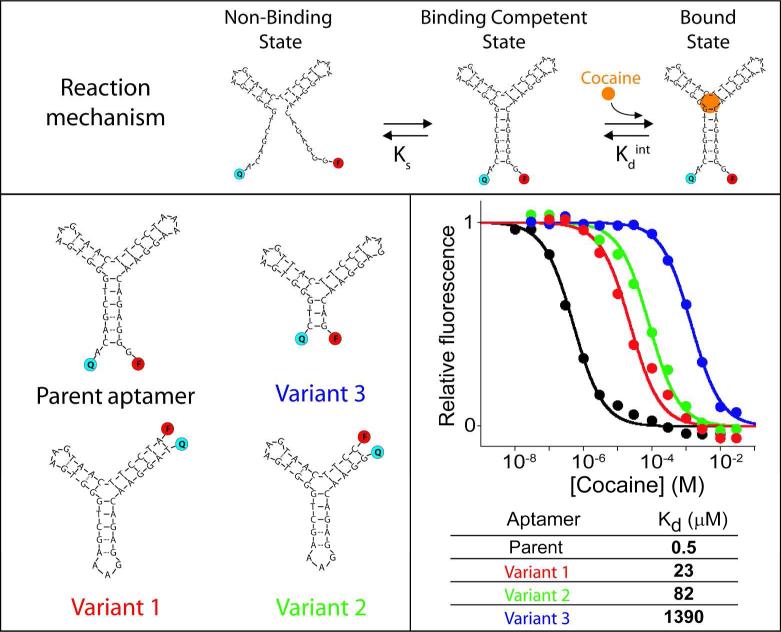
Figure 2.
Tuning affinity of an aptamer by using distal site mutations to alter its conformational switching equilibrium constant. We designed variants of the cocaine-binding aptamer that likely display lower switching equilibrium constant (and thus weaker overall affinity) by changing the parent oligonucleotide sequence to destabilize the aptamer's target-binding conformation. By doing so we obtained a series of aptamers (only four shown here; see other variants in Figure S1), with affinity constants spanning more than 3 orders of magnitude. Variant 1: a circular permutant; variant 2: a truncation of that circular permutant; variant 3: a truncation of the parent sequence. As expected for single-site binding, the useful dynamic ranges of all these variants span the characteristic 81-fold range of target concentration.