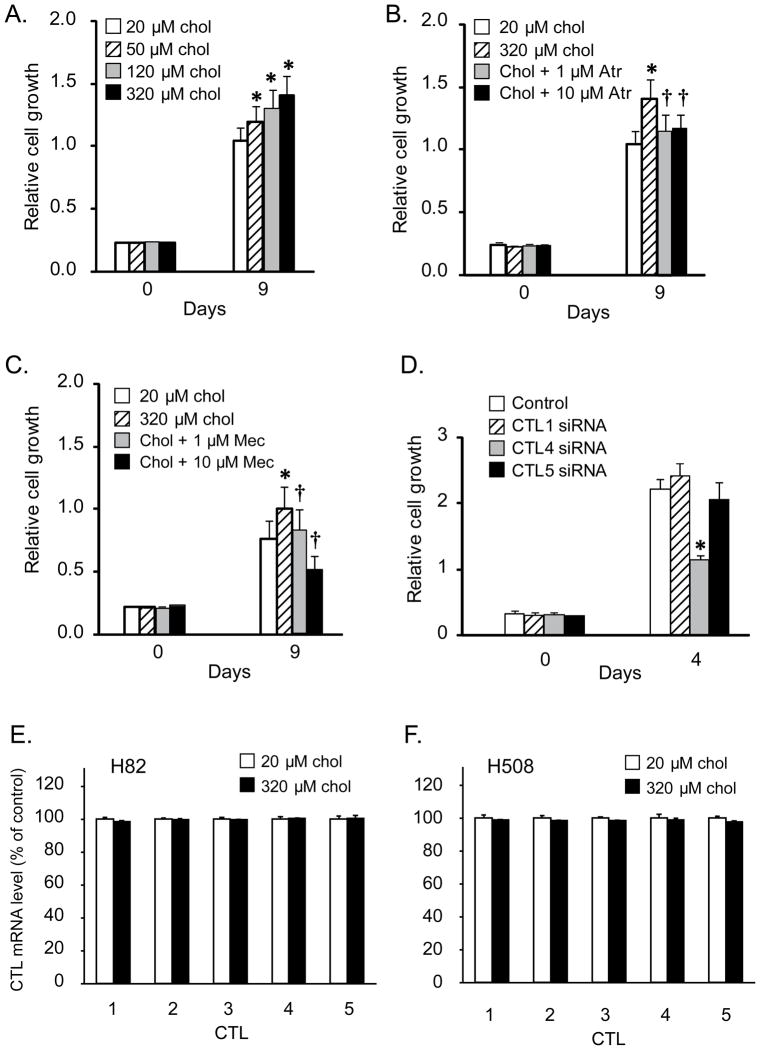
Figure 6.
Modulation of SCLC cell growth by choline and cholinergic receptor antagonists. H82 cells were plated as described in the material and methods. Drugs were added immediately after plating cells and incubated for 9 days as described in methods. A. Choline caused a concentration-dependent increase of H82 cell proliferation at 9 days (* P < 0.05). B. The mAChR antagonist atropine at 1 and 10 μM inhibited the increase of H82 cell proliferation induced by increased choline (320 μM). C. The nAChR antagonist mecamylamine at 1 and 10 μM inhibited the increase of H82 cell proliferation induced by increased choline (320 μM). Data were mean ± SE of 12 replicates in two separate experiments. * p< 0.05 versus baseline choline. † p<0.05 versus 320 μM choline alone. chol, choline; Atr, atropine; Mec, mecamylamine. D. Effect of CTL knockdown on H82 cell growth (choline concentration = 20 μM). Consistent with the effects of CTL knockdowns on ACh secretion shown in panel C, knockdown of CTL4 significantly decreased H82 cell growth while knockdown of CTL5 had no effect and knockdown of CTL1 had a small stimulatory effect. Data were mean ± SE of 20 replicates in two separate experiments. *P<0.05 compared to the cells treated with control siRNA. E., F. Increased levels of choline did not affect levels of CTL expression in either H82 or H508 cells.