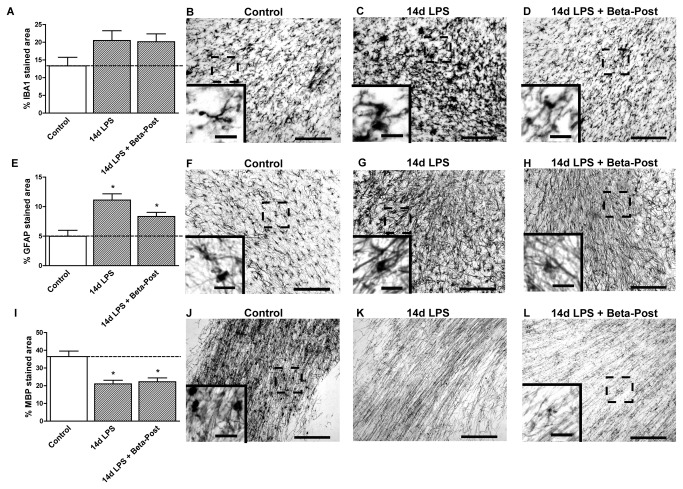
Figure 6. Effect of intra-amniotic LPS and antenatal glucocorticoid exposure 14 days before delivery on the subcortical white matter.
A: The area fraction (%) of IBA1 immuno-reactivity did not change after intra-amniotic LPS and/or betamethasone exposure 14 days before delivery. B-D: Representative images of the IBA1 staining in the SCWM in controls (B), 14d LPS (C) and 14d LPS + Beta-Post (D) exposed animals. E: LPS exposure 14 days before delivery significantly increased the area fraction (%) of GFAP immuno-reactivity irrespective of betamethasone post-treatment. F-H: Representative images of the GFAP staining in the SCWM in controls (F), 14d LPS (G) and 14d LPS + Beta-Post (H) exposed animals. I: The area fraction (%) of MBP immuno-reactivity decreased 14 days after intra-amniotic LPS exposure irrespective of betamethasone treatment compared to controls. J-L: Representative images of the MBP staining in the SCWM in controls (J), 14d LPS (K) and 14d LPS + Beta-Post (L) exposed animals. Scale bar = 200 µm; scale bar insert = 25 µm. *p<0.05 versus controls using a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.