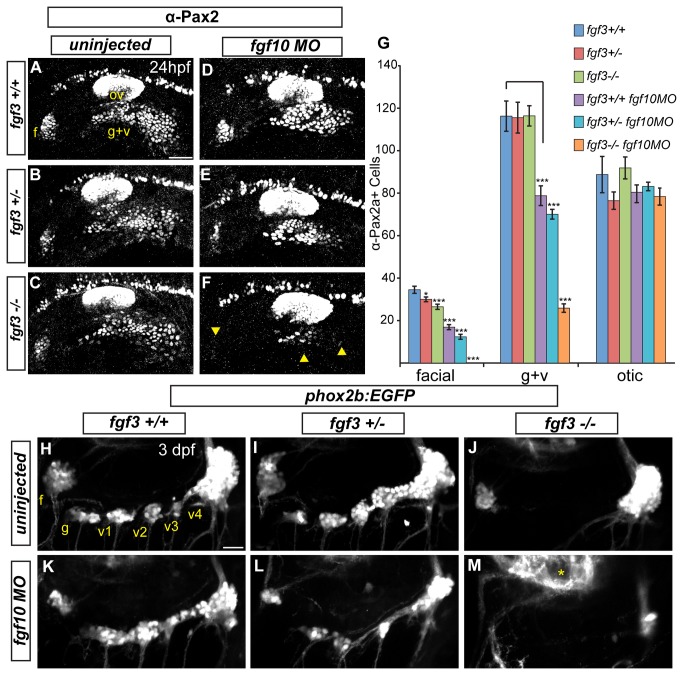
Figure 2. Fgf3 and Fgf10a are required for maturation of epibranchial placodes and development of the epibranchial ganglia.
(A-C) Confocal projections showing Pax2a expression in wild-type (A) fgf3+/- (B) and fgf3-/- (C) embryos at 24 hpf. (D-F) Confocal projections showing Pax2a expression in 24-hour old wild-type (D) fgf3+/- (E) and fgf3-/- (F) embryos injected with fgf10a-MO. Note the significant loss of Pax2a expression in the EB placodes (F; arrowheads). (G) Pax2a+ cell number in the facial, glossopharyngeal/vagal, and otic placodes for conditions in (A-F). Note the complete loss of Pax2a+ cells in the facial placode and a 4.5 fold reduction in the glossopharyngeal/vagal placode in fgf3-/-;fgf10a-MO embryos (ANOVA multiple comparison with Bonferroni’s correction; *P<0.05; ***P<<0.001; Error bars: standard error of mean; n=11 embryos per condition). (H-M) Confocal projections of 3 dpf wild-type (H), fgf3+/- (I) and fgf3-/- (J) embryos and wild-type (K), fgf3+/- (L) and fgf3-/- (M) embryos injected with fgf10a-MO. All embryos contain TgBAC(phox2b:EGFP) which marks EB ganglia. Note the loss of EGFP expression in the glossopharyngeal and three small vagal ganglia in fgf3-/- embryos (J) and the complete loss of EGFP expression in all EB ganglia in fgf3-/-;fgf10a-MO with the exception of a few EGFP+ cells in the region of the large vagal ganglion (M). Asterisk marks hindbrain neurons also expressing TgBAC(phox2b:EGFP). Abbreviations: f, facial placode (A) or facial ganglia (H); ov, otic vesicle; g+v, glossopharyngeal/vagal placode; g, glossopharyngeal ganglia; v1-v3, small vagal ganglia 1-3; v4, large vagal ganglion. Scale bars: 50 µm (A); 25 µm (H).