Figure 2.
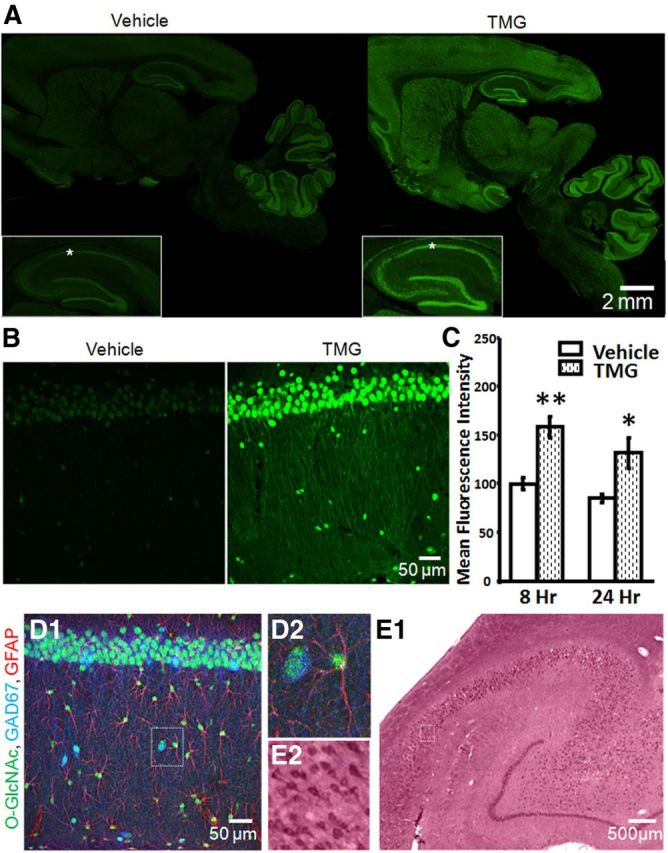
Protein O-GlcNAcylation is ubiquitous and is increased by in vivo thiamet-G-treatment. A, O-GlcNAc staining (green) in sagittal brain sections from Vehicle- and TMG-injected (10 mg/kg) rats 8 h post injection including hippocampal formation (inset) and area CA1 (asterisks; 10× magnification). B, O-GlcNAcylated proteins are increased in area CA1 of rat hippocampus 8 h post TMG injection (40× magnification). C, Quantification of mean fluorescence intensity in area CA1 from Vehicle- and TMG-treated rats, 8 h (Vehicle: n = 5, TMG: n = 7) and 24 h (Vehicle: n = 4, TMG: n = 3) post intraperitoneal injection. D1, O-GlcNAcylated proteins (green) are located in CA1 pyramidal cells, inhibitory interneurons (blue), and astrocytes (red; 40× magnification). D2, Boxed area in D1 showing an O-GlcNAc-positive astrocyte and inhibitory interneuron. E1, O-GlcNAcylated proteins detected in human hippocampus (20× magnification). E2, Boxed area in E1 showing O-GlcNAc-positive CA1 pyramidal cells. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.001. Error bars indicate SEM.
