Figure 9.
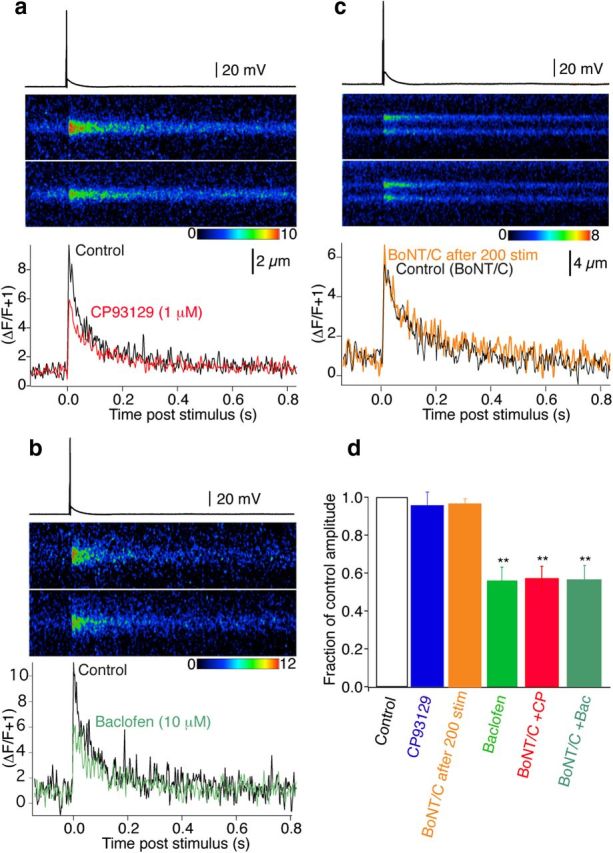
BoNT/C reveals 5-HT1B receptor-mediated inhibition of presynaptic Ca2+ transients. CA1 pyramidal neurons were recorded with electrodes containing BoNT/C, Alexa, and Fluo-5F. Two hundred action potentials (1 Hz, 35 min post whole cell) eliminated primed vesicles before recording. a, Action potential-evoked Ca2+ transients recorded by line scanning over CA1 pyramidal neuron presynaptic varicosities in the subiculum (top trace Control, bottom in CP93129; 1 μm). Graph (bottom) shows the integrated signals of three averaged responses in Control (black) and CP93129 (1 μm; red). b, Similar CA1 presynaptic varicosity recording before (Control, black) and in baclofen (10 μm; green) also after perfusion with BoNT/C. c, Similar CA1 presynaptic Ca2+ transient before (Control BoNT/C, black) following infusion of dyes and BoNT/C, and after 200 stimuli (BoNT/ after 200 stim, orange) Stimuli to exhaust the primed vesicle pool did not significantly alter the time course or amplitude of the transient. d, Summary of BoNT/C and GPCR effects on Ca2+ transients (orange, 200 stimuli after BoNT/C application, n = 3; blue, CP93129, n = 8; green, baclofen, n = 7) both in Control conditions. Then after priming eliminated with BoNT/C (red, CP93129, n = 5; dark green, baclofen, n = 4). BoNT/C revealed reduction of Ca2+ transients in CP93129. **p < 0.01.
