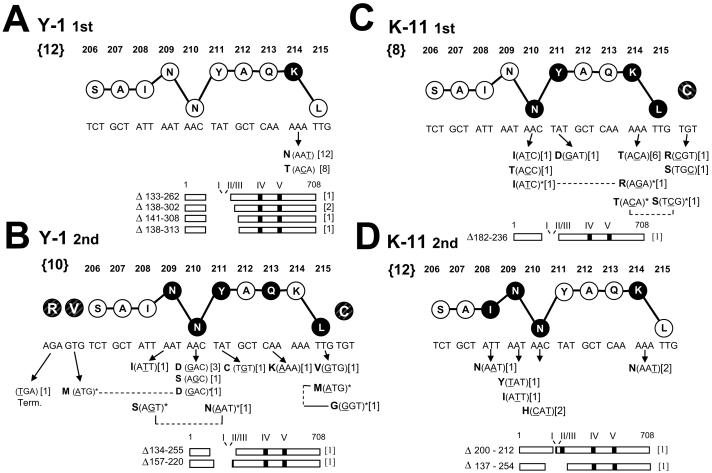
Fig. 2.
Alterations affecting epitope I identified following selection with the CTL clones Y-1 (A, B) or K-11 (C, D). A, first Y-1 selection. B, second Y-1 selection. C, first K-11 selection. D, second K-11 selection. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences (single letter abbreviations) for an epitope I 10mer peptide are shown. The vertical location of each residue in the stick and ball representation implies function within the epitope peptide based on previous studies (Lippolis et al., 1995): residues implicated in peptide-MHC binding are lowered; residues involved in TCR recognition are raised. Darkened circles indicate residue positions at which substitutions were identified in this study; nucleotide alteration(s) and predicted amino acid substitutions are shown below the corresponding residue position (arrows). Deletions affecting epitopes are illustrated by diagrams of the 708 residue T ag, and the residues lost by each deletion are indicated. Numbers not within brackets indicate residue positions within the wild type T ag. Bold numbers within the “{}” brackets to the left of the wild type epitope sequences indicate the total number of selection cultures from which resistant populations arose. Numbers in brackets to the right of each substitution or deletion shown below the ball and stick epitope sequence indicate the number of selection cultures in which that substitution or deletion was detected. Positions of altered adjacent flanking residues (shaded and crosshatched, but not connected by lines to the epitope I residues 206-215) are included in (B) and (C). Residue positions altered in doubly mutated epitope sequences are connected by the dashed lines and indicated by asterisks. The epitope I mutations are also presented Figure 4 grouped by the variant populations in which they were identified.