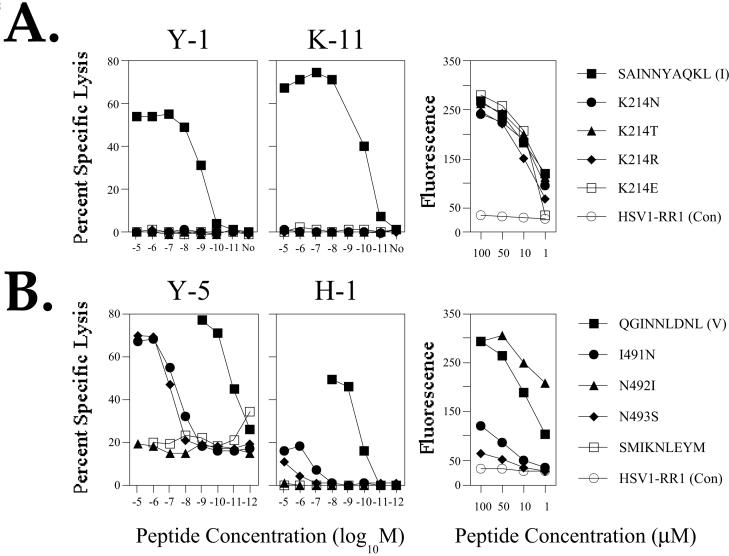
Fig. 6.
Target cell lysis by CTL clones and H-2Db stabilization for synthetic peptides corresponding to substituted epitope I or V sequences. RMA cells pulsed with substituted variant peptides at the concentrations indicated in the figure were combined with the CTL clones Y-1 or K-11 (A), or H-1 or Y-5 (B) in standard cytotoxicity assays (left two panels in A or B). No, no peptide added. The SMIKNLEYM peptide that efficiently binds H-2Db molecules, but is not recognized by T ag-specific CTL clones, was used as a control in assays utilizing the epitope V-specific CTL clones. RMA/s cells pulsed with varying concentrations of variant epitope I (A) or epitope V (B) peptides at the concentrations indicated in the figure were analyzed by flow cytometry following staining for cell surface H-2Db complexes using the conformation-sensitive monoclonal antibody 28-14-8. A peptide corresponding to an H-2Kb-restricted Herpes simplex virus epitope (HSVI-RR1) was used as a non-stabilizing control (Con).