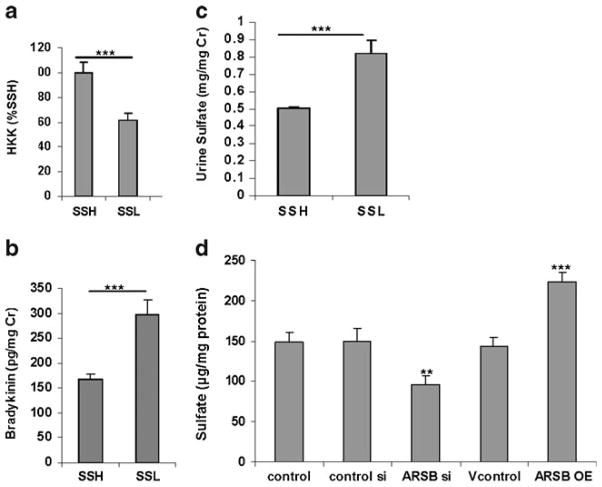
Fig. 3.
Renal tissue kininogen increased, and urinary bradykinin and sulfate reduced following high salt. a. High-molecular weight kininogen (HKK) was measured by ELISA in the SSH and SSL renal tissue, and was significantly greater in the SSH tissue (p<0.0001; n=10 for SSH and SSL). b. Bradykinin was measured in the urine of the SSH and SSL rats on high and low salt diets, respectively. Bradykinin values were significantly less in the SSH group (p<0.0001; n=10 for SSH and SSL). c. Urinary sulfate was significantly less in the 24-hour urine of the SSH rats, compared to the SSL rats (p<0.0001; n=6 for SSH and n = 6 for SSL). d. Sulfate content in the spent media from the NRK cells declined following silencing of ARSB by siRNA, from a baseline value of 148±13 μg/mg protein to 96±11 μg/mg protein (p< 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post-test) and increased following overexpression of ARSB to 223±12.5 μg/mg protein (p< 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Tukey-Kramer post-test). [HKK = high molecular weight kininogen; SSH = salt-sensitive on high salt; SSL = salt-sensitive on low salt diet; ARSB = arylsulfatase B; NRK = normal rat kidney]