Fig. 4.
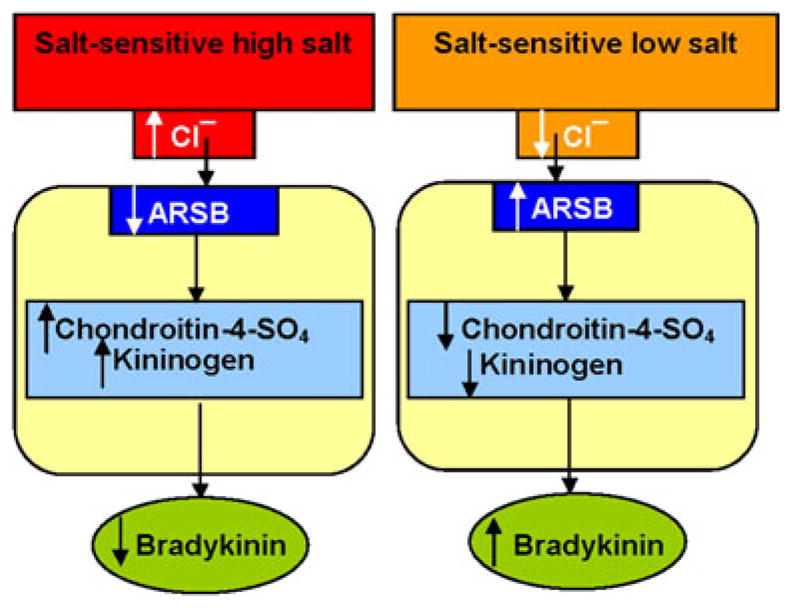
Schematic representation of the relationships between ARSB activity, chloride exposure, chondroitin-4-sulfation, kininogen, and bradykinin. The drawing depicts the impact of high vs. low salt exposure on the ARSB activity, chondroitin-4-sulfate content, cell-bound kininogen, and bradykinin in the rat kidney tissue. Higher chloride exposure leads to reduced ARSB activity, which leads to increase in chondroitin-4-sulfate (C4S) with increased binding of kininogen with C4S, producing a reduction in secreted bradykinin
