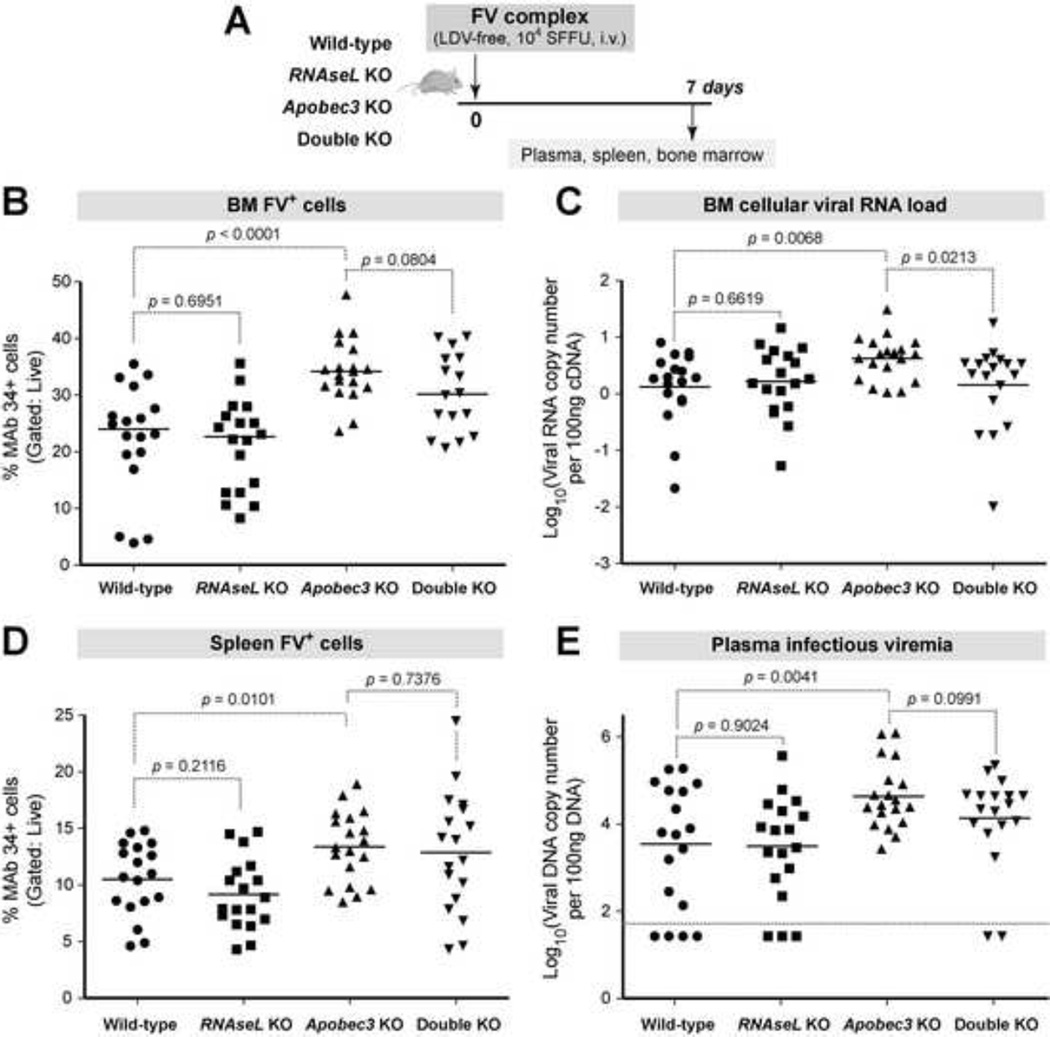
Fig. 2. RNaseL does not significantly impact acute FV infection even in the absence of Apobec3.
(A) Infection timeline. WT, RNaseL KO, Apobec3 KO, and RNaseL/Apobec3 double KO mice were sacrificed at 7 dpi for analyses. Data were pooled from 3 independent infection cohorts. (B) BM FV+ cells. Glyco-Gag+ cells were stained with MAb 34 and the percent of FV infected cells was determined by flow cytometry. (C) BM cellular viral RNA load. RNA was extracted from BM and qPCR was used to determine FV RNA copies, normalized to beta-actin mRNA copies. Log10 values are shown. (D) FV Glyco-Gag+ splenocytes, stained for flow cytometry as in (B). (E) Infectious plasma viremia. Plasma (5 µl) were inoculated into Mus dunni cells, and after 48 h, DNA was extracted and qPCR was used to determine the amount of FV DNA. Data was normalized to 100 ng of DNA input. Log10 values are shown. Dashed lines correspond to the detection limit of the assay. For all panels, each dot corresponds to an infected mouse, bars correspond to mean values. Differences between pairs of experimental groups were evaluated using 2-tailed Student’s t test, with p<0.05 considered statistically significant.