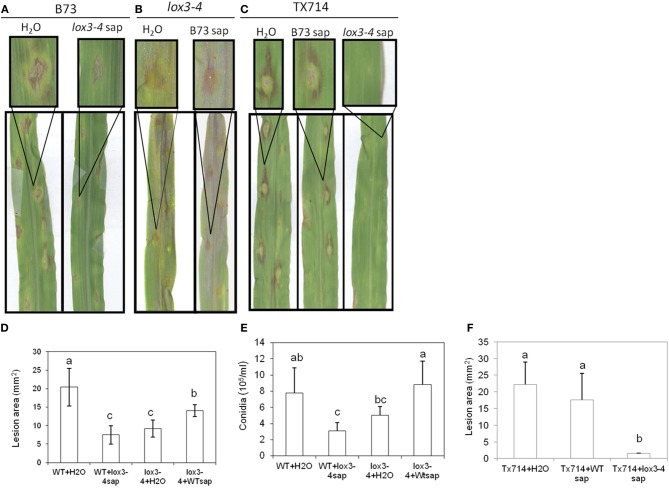
Figure 3.
Effect of xylem sap from lox3-4 mutant and B73 NIL plants on the pathogenicity of C. graminicola infected on the leaves. The xylem sap were collected from approximately 3-week-old lox3-4 mutant and B73 seedlings at 4 true leaf stage by cutting the stem from the position above the soil. Twenty microliter of sap per plant was injected into the wounding site on the stem of lox3-4 mutant and B73 or TX714 NIL, respectively, subsequently followed by the infection with C. graminicola at 1 × 106 spores/ml. The disease symptoms were recorded and photographed at 3 days post infection on (A) B73 plants treated with H2O or lox3-4 xylem sap, (B) lox3-4 plants treated with H2O or B73 sap, and (C)TX714 plants treated with H2O, B73 sap, or lox3-4 xylem sap. The insert panels show the close-up of representative lesions showing on the corresponding leaf. The (D) lesion size and (E) number of conidia on lox3-4 and B73 leaves infected with C. graminicola upon treatment H2O, and lox3-4 or B73 sap and (F) lesion size on TX714 leaves infected with C. graminicola upon treatment H2O, and lox3-4 or B73 sap. The data are shown as mean ± SE (n > 15 for lesion size and n = 3 for conidia number experiments, respectively). The different letters above the bar indicate the significant difference between different treatments analyzed by SPSS software One-Way ANOVA (p < 0.05).