Abstract
Human steroid hormone biosynthesis is the result of a complex series of chemical transformations operating on cholesterol, with key steps mediated by members of the Cytochrome P450 superfamily. In the formation of the male hormone dehydroepiandrosterone, pregnenolone is first hydroxylated by P450 CYP17A1 at the 17-carbon followed a second round of catalysis by the same enzyme that cleaves C17–C20 carbon-carbon bond releasing acetic acid and the 17-keto product. In order to explore the mechanism of this C-C “lyase” activity we investigated the kinetic isotope effect on the steady state turnover of Nanodisc incorporated CYP17A1. Our experiments revealed the expected small positive (~1.3) isotope effect for the hydroxylase chemistry. However, a surprising result was the large inverse isotope effect (~0.39) observed for the carbon-carbon bond cleavage activity. These results strongly suggest that the P450 reactive intermediate involved in this latter step is an iron-bound ferric peroxoanion.
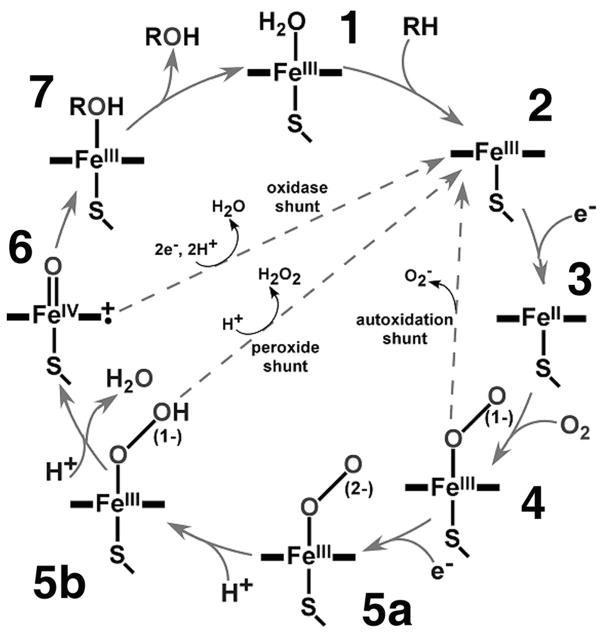
Since the discovery of cytochrome P450s by Omura and Sato this large superfamily of heme containing monooxygenases has yielded a rich tapestry of substrate specificities and chemical transformations.1,2 Noteworthy is the facile hydroxylation of unactivated carbon centers, with the P450s cycling through a series of iron-oxygen intermediates following electron input to a ferrous dioxygen adduct.3 Carbon center functionalization is considered to occur via the “Groves rebound mechanism”.4 First, the ferric resting state of the enzyme (Figure 1) is reduced by one electron transfer from an associated redox partner with subsequent binding of atmospheric dioxygen to form the ferrous-O2 complex which is reduced by a second electron to form the key peroxoanion intermediate. Active site mediated proton transfer generates the iron-bound hydroperoxo which undergoes O-O bond scission to release water and generate an Fe(IV)O porphyrin cation radical “Compound 1” intermediate which then initiates hydrogen abstraction from the substrate and radical recombination to form product.3 A major accomplishment in recent years has been the isolation and spectroscopic characterization of the peroxoanion [5a], hydroperoxoferric [5b] and “Compound 1” [6] intermediates in various P450 systems. 5–8
Figure 1.
The P450 catalytic cycle engaged in Compound 1 mediated oxidation chemistry, noting unproductive pathways.
More circumspect in steroid metabolism is the subsequent reaction by P450 CYP17A1 which involves scission of the 17–20 carbon-carbon bond, releasing acetic acid and forming a ketone at the apex of the D-ring of the cholesterol backbone. The mechanism of this C-C “lyase” activity has been subject of considerable debate for many years and yet the reactive intermediate responsible for 17,20 lyase chemistry remains undefined.9 Early work by Ahktar et al. suggested a heme-bound unprotonated peroxoanion [5a] acting through nucleophilic attack on the C-20 carbonyl of 17α-OH pregenenolone (OH-PREG) creating a hemi-acetyl that would decay through homolytic or heterolytic scission of the iron ligated acyl peroxo to form the products of the reaction.10 Alternatively, a radical mechanism involving the standard Compound 1 intermediate [6] has been proposed.11 These two pathways are distinguished by the involvement of protons in the standard mechanism involving Compound 1 (Cpd1) formation, as seen in Figure 1.
In this communication, we report investigation of kinetic solvent isotope effects on the steady state turnover of CYP17A1 in both its hydroxylase and lyase functionalities. We reasoned that this technique would distinguish between the traditional Cpd1 mediated catalysis, which relies on at least two protons to generate the high valent iron-oxo species and a nucleophilic reactivity of a ferric peroxoanion intermediate before proton involvement in O-O bond scission.
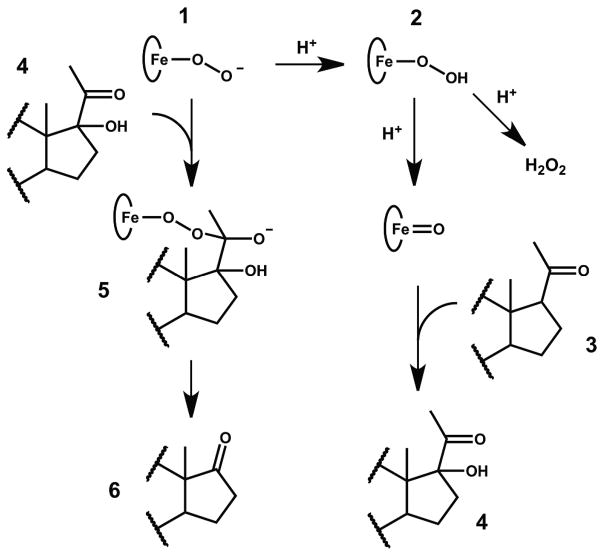
An additional concern in comparing these two pathways of androgen formation are uncoupling reactions which release hydrogen peroxide. While the hydroxylation of pregnenolone (PREG) at the 17-position is relatively well coupled, it is known that when OH-PREG is a substrate and the formation of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) is monitored, much of the pyridine nucleotide reducing equivalents appear in free hydrogen peroxide rather than carbon product.12 Uncoupling occurs from the iron-peroxide intermediates and can also involve protons. We thus have the following branching pathways (Figure 2) where the addition of two protons to the ferric peroxoanion [1] results in formation of Cpd1 which is utilized in the hydroxylation of pregnenolone [3] to OH-PREG [4] in the first step of CYP17 catalysis. The second, uncoupled step responsible for androgen formation, either proceeds productively from [1] through an acyl-peroxo intermediate [5] to form DHEA [6], or unproductively through proton dependent formation of [2] and ultimate release of peroxide.
Figure 2.
Isotopically sensitive branching between the peroxo- and hydroperoxoferric species during CYP17 mediated catalysis.
In order to generate a soluble, homogeneous and monodisperse version of the membrane associated CYP17A1, the Nanodisc system was used. This technology has found wide application for numerous membrane proteins in general and for the cytochromes P450 in particular.13,14 Product formation and NADPH oxidation rates of human CYP17A1 incorporated into Nanodiscs in the presence of its redox partner cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (CPR) and its allosteric effector cytochrome b5 were measured in the presence of saturating concentrations of PREG and OH-PREG at 37°C and pH/pD 7.4 (see SI for full experimental details). Deuterated samples were made by exhaustive exchange of the proteins in D2O.
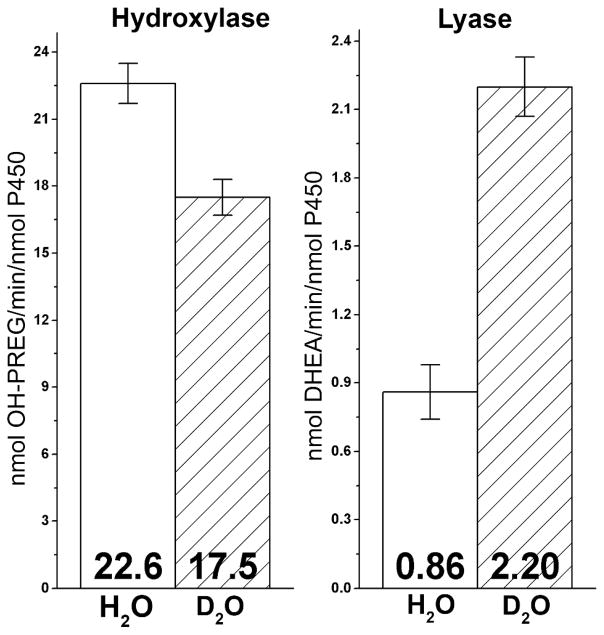
When PREG is a substrate, the rate of 17α-hydroxylated product formation occurred at a rate of 22.6 ± 0.9 min−1, while in deuterated buffer this rate slowed to 17.5 ± 0.8 min−1. This corresponds to a kinetic solvent isotope effect (KSIE) for the hydroxylation reaction of kH/kD = 1.3, very similar to values reported for other P450 systems catalyzing hydroxylation chemistry.15–17
When OH-PREG is used as a substrate, the rate of conversion of the α-hydroxy ketone to DHEA via C-C lyase activity was much slower, as previously documented for this system.18,19 Unexpectedly, however, when D2O was substituted for H2O, the rate of product formation was dramatically augmented, from 0.86 ± 0.1 min−1 to 2.2 ± 0.1 min−1. This corresponds to an inverse KSIE of 0.39. (Figure 3)
Figure 3.
Steady state kinetic solvent isotope effects observed for hydroxylase and lyase CYP17 catalysis. Rates are expressed in nmol product/min/nmol P450.
In addition to product formation, the overall rate of NADPH oxidation also monitors the uncoupling pathway wherein reducing equivalents appear as released hydrogen peroxide without substrate metabolism. Despite the inverse KSIE seen in the product forming rate, the rate of NADPH oxidation was decreased by 40%, from 27.5 ± 0.6 min−1 to 16.6 ± 0.3 min−1. This difference is also reflected in the absence of substrate, where rates in H2O and D2O were 31.5 ± 0.7 min−1 and 18.1±1.0 min−1, respectively. This normal slowing of rates in the presence of D2O versus H2O is another important indicator of the intermediates involved in lyase chemistry. The same rate decrease in D2O as compared to H2O in the substrate-free CYP17A1 suggests the same rate-limiting step for the overall steady-state NADPH consumption kinetics that is strongly dependent on protonation. This protonation step is likely to be the first protonation of peroxoanion coordinated to the heme iron. The alternative suggestion of the second protonation event and formation of Cpd1 as the rate limiting step can be rejected as incompatible with the different signs of KSIE observed in hydroxylation of PREG and lyase reaction with OH-PREG as substrate. If formation of Cpd1 would be the rate-limiting step, the KSIE of lyase reaction would be higher or equal to one, depending on the masking by other steps in the catalytic cycle.
The hydroxylase activity of CYP17A1 is expected to proceed through the classical Groves rebound mechanism with Cpd1 as the reactive intermediate. Results for this first reaction are entirely consistent with expectations of a partially masked, proton dependent, Cpd1 mediated mechanism, and are congruent with previous reports of solvent isotope effects in P450cam which also utilizes an oxene intermediate.15,17 The large inverse isotope effect and decrease in NADPH oxidation rate for the latter lyase reaction where OH-PREG is subjected to 17,20 C-C bond cleavage to form DHEA, however, cannot be reconciled with a Cpd1 mediated reaction. Rather, these observations are consistent with inhibition of protonation of the peroxo-ferric species in a manner that serves to facilitate productive, rather than unproductive oxidation. Formation of the peroxo-ferric intermediate and nucleophilic attack of C-20 carbonyl does not involve any protonation event and is expected to exhibit the same kinetics in H2O and D2O. Alternatively, two protonation steps with concomitant formation of the hydroperoxo-ferric complex and Cpd1 progress much slower in D2O. Because of this difference in rates between productive and unproductive pathways at the peroxo-branching point the steady-state concentration of this intermediate increases and the apparent rate of product formation also increases in D2O, although the microscopic catalytic rate is the same in both solvents. Such mechanism is also confirmed by significant decrease of NADPH consumption rate in D2O, indicating smaller fraction of reducing equivalents following proton-dependent pathways of hydrogen peroxide formation from hydroperoxo-ferric intermediate and oxidase reaction of Cpd1.
Similar mechanistic studies in other enzymes also reported inverse solvent isotope effect as the result of slower uncoupling reaction that competed with the productive pathway. This was the case in tyrosine hydroxylase, where uncoupling pathway via the breakdown of peroxypterin intermediate with formation of H2O2 can be compared to the release of peroxide in cytochrome P450 catalytic cycle and to uncoupling in flavin monooxygenases.20,21 Another example of improved product formation in steady-state is the reaction catalyzed by putidamonooxin caused by considerable inhibition of uncoupling channel in D2O was studied by Twilfer et al.22 In this work, the uncoupling reaction afforded peroxide release and thus required protonation. In D2O this protonation was significantly slower and as a result, partitioning of the active intermediate between productive and unproductive pathways was shifted in favor of the former. This example of directly observed competition between the productive (monooxygenase and dioxygenase reaction) and unproductive (protonation of active oxygen species and formation of H2O2 in uncoupling pathway) pathways of this enzyme was interpreted as indicating the iron-peroxo complex as an active intermediate in putidamonooxin.
The normal KSIE for hydroxylation reaction and strong inverse apparent KSIE for the lyase reaction catalyzed by CYP17A1 cannot be reconciled with the same rate-limiting protonation dependent step commonly observed in other cytochromes P450 when Cpd1 is the main catalytic intermediate. Rather, an inverse KSIE implies catalysis via a proton-independent intermediate and the presence of the branching proton-dependent uncoupling pathway, which is considerably slower in D2O, thus providing higher yield of the product. Taken together, these results provide the strong experimental evidence of two distinct mechanisms for the first and the second steps of CYP17A1 catalyzed reactions.
These results highlight a novel property of the CYP17A1 active site: the ability to select between use of multiple reactive intermediates based on presence of a 17α-hydroxy moiety on the substrate molecule. In the presence of pregnenolone, this enzyme preferentially catalyzes formation of OH-PREG in a straightforward Cpd1 mediated mechanism known to function in other P450s. However, when OH-PREG is used as a substrate, our observations strongly implicate the peroxoanion as the reactive intermediate.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grant GM31756 to S.G.S.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Experimental details and additional data. This material is available free of charge via the Internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
References
- 1.Omura T, Sato R. J Biol Chem. 1964;239:2370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cytochrome P450: Structure, Mechanism, and Biochemistry. 3. Kluwer/Plenum; New York: 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Denisov IG, Makris TM, Sligar SG, Schlichting I. Chem Rev. 2005;105:2253. doi: 10.1021/cr0307143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Groves JT. J Inorg Biochem. 2006;100:434. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2006.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Denisov IG, Mak PJ, Makris TM, Sligar SG, Kincaid JR. J Phys Chem A. 2008;112:13172. doi: 10.1021/jp8017875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gantt SL, Denisov IG, Grinkova YV, Sligar SG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;387:169. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.06.154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rittle J, Younker JM, Green MT. Inorg Chem. 2010;49:3610. doi: 10.1021/ic902062d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rittle J, Green MT. Science. 2010;330:933. doi: 10.1126/science.1193478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Akhtar M, Wright JN, Lee-Robichaud P. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2011;125:2. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.11.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Akhtar M, Corina DL, Miller SL, Shyadehi AZ, Wright JN. Journal of the Chemical Society-Perkin Transactions. 1994;1:263. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Akhtar M, Corina D, Miller S, Shyadehi AZ, Wright JN. Biochemistry. 1994;33:4410. doi: 10.1021/bi00180a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brock BJ, Waterman MR. Biochemistry. 1999;38:1598. doi: 10.1021/bi9821059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Denisov IG, Sligar SG. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011;1814:223. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.05.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Luthra A, Gregory M, Grinkova YV, Denisov IG, Sligar SG. Methods in molecular biology. 2013;987:115. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-321-3_10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Vidakovic M, Sligar SG, Li H, Poulos TL. Biochemistry. 1998;37:9211. doi: 10.1021/bi980189f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Liu Y, Ortiz de Montellano PR. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:5297. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.8.5297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Batabyal D, Li H, Poulos TL. Biochemistry. 2013;52:5396. doi: 10.1021/bi400676d. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Usanov SA, Gilep AA, Sushko TA. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta-Proteins and Proteomics. 2011;1814:200. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2010.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Imai T, Globerman H, Gertner J, Kagawa N, Waterman M. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1993;268:19681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Frantom PA, Fitzpatrick PF. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:16190. doi: 10.1021/ja0383165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Massey V. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:22459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Twilfer H, Sandfort G, Bernhardt FH. European Journal of Biochemistry. 2000;267:5926. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.