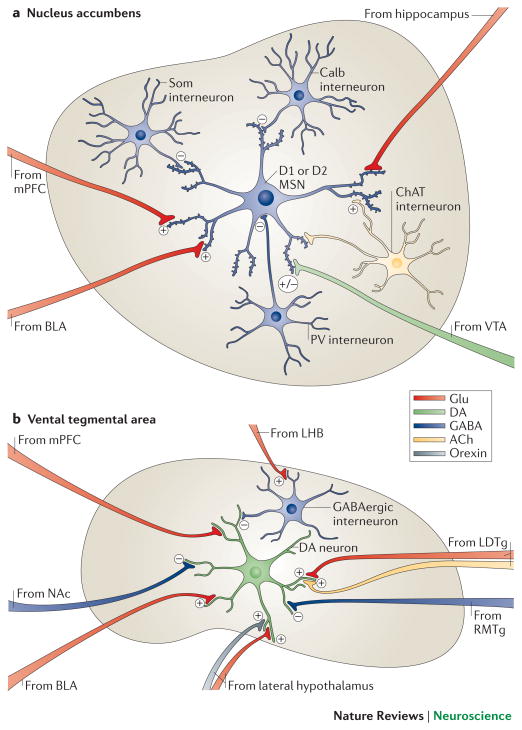
Figure 2. Local microcircuitry of the NAc and VTA.
a | A close-up view detailing the presynaptic inputs onto D1- and D2-type GABAergic medium spiny neurons (MSNs) and onto several types of interneurons within the nucleus accumbens (NAc). The latter include GABAergic interneurons that express calretinin, (Calr), parvalbumin (PV), somatostatin (SOM) or calbindin (Calb), and large cholinergic interneurons that express choline acetyltransferase (ChAT). Glutamatergic neurons (Glu) from the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), hippocampus (Hipp) and basolateral amygdala (BLA) release glutamate onto spine synapses to provide excitatory signals to GABAergic MSN projection neurons. These excitatory inputs also synapse directly onto the GABAergic and cholinergic interneurons that modulate MSNs (not shown). D1-and D2-type MSNs also receive signals from dopamine though shaft or spine neck synapses (brown). The figure does not depict possible differences in glutamatergic innervation of D1-type versus D2-type MSNs, which are only now beginning to be explored. b | A close-up view detailing the presynaptic inputs onto ventral tegmental area (VTA) dopamine neurons and local GABAergic interneurons in the VTA. Glutamatergic neurons (Glu) from the amygdala (BLA), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and lateral dorsal tegmentum (LDTg) synapse directly onto VTA dopamine neurons. In contrast, glutamatergic neurons from lateral habenula (LHb) synapse directly onto inhibitory GABAergic neurons in the rostromedial tegmentum (RMTg) or VTA proper, which then inhibit dopamine neurons and promote aversion. Dopamine neurons receive direct excitatory inputs from peptidergic (e.g., orexinergic) or glutamatergic neurons in lateral hypothalamus (LH), which increase dopamine release and promote reward. Although GABAergic projections from the NAc are shown innervating VTA dopamine neurons, much of this innervation is on VTA GABAergic neurons, whereas much of the GABAergic innervation of the dopamine neurons is indirect, via GABAergic neurons in ventral pallidum (not shown). Color code: dopaminergic=green; glutamatergic=red; GABAergic=blue; peptidergic=yellow; and cholinergic=orange.