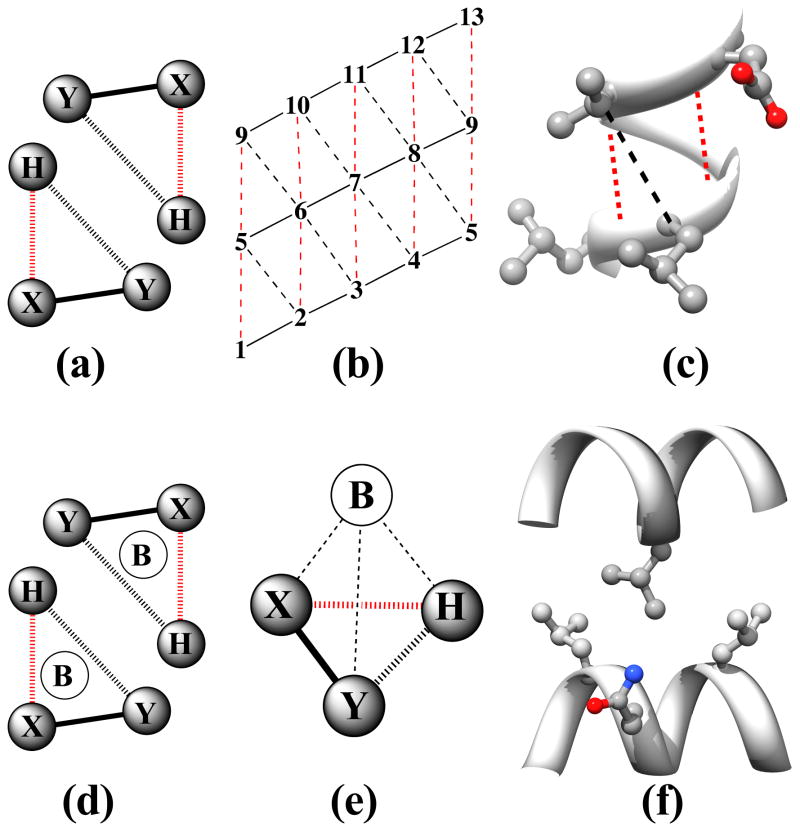
Figure 2. The Knob-Socket Motif.
Based on the original definition from previous work,1 a knob-socket RPC involves 4 residues from 2 α-helices, where all side chains pack against each other in a 3+1 configuration. The 2:1+1 indicates that a 3 residue socket local to one α-helix pack with the 1 residue knob on the other α-helix. Helix representations were created using Chimera.123 (a) A two-dimensional representation of the RPC socket shows the 3 residues X, Y, and H. While the residues’ side-chains all pack against each other, the main-chain interactions differ as indicated by the lines. The i to i+4 α-helical hydrogen bond (broken red line) connects X and H. Consecutive residues X and Y share a peptide bond (solid black line). Residues Y and H only pack with their side-chains (broken black line). (b) The modified version of Crick’s43 α-helical lattice showing the 2 types of socket RPCs on the α-helix surface. Residues on the edge wrap to display all possible sockets of the α-helix. The first in the lower left corner is a low X or XY:H socket, where the X residue is the lowest position in the sequence. The next socket is a high X or H:YX socket, where the X residue is the highest position in the sequence. In helix there is always an alternating pattern of these 2 sockets. (c) The low and high X sockets are shown on an α-helix structure from kinase 2ra7.95 The low X consists of LL:V and the high X consists of D:LV. In this case the covalent bonds are replaced by the ribbon trace, but the other bonds are the same. Residues i and i+5 clearly cannot contact as they face away from each other. (d) A two-dimensional representation of the knob-socket motif shows the 3 residues in the socket are all packed against a knob residue B from the other helix. (e) The tetrahedral arrangement of the 4 residue knob-socket motif is shown, where residues are reduced to spheres for clarity. The knob residue B contacts all the 3 socket residues only through side-chain interactions (broken black lines). (f) The knob-socket motif shown between 2 α-helices.95 On one α-helix, a low X socket of LQ:L packs against the knob B residue L from the other α-helix.