Abstract
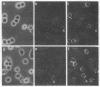
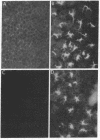
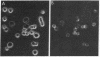
Murine epidermal Langerhans cells were analyzed with fluorescence microscopy and multicolor flow cytometry for the surface expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II antigens. Langerhans cells of H-2k haplotype were identified in situ or in epidermal-cell suspensions by their surface expression of the MHC class II determinants I-Ak and I-Ek. More than 90% of class II-positive Langerhans cells in epidermal-cell suspensions expressed no or barely detectable amounts of MHC class I antigens. Quantitation by flow cytometry revealed that H-2k Langerhans cells expressed only 1.6-3.3% as much H-2Kk as did class II-negative keratinocytes in the same epidermal-cell suspensions. By fluorescence microscopy, class I MHC antigens were not detectable on Langerhans cells in situ when analyzed on sheets of intact epidermis. The deficient expression of class I MHC permitted highly purified Langerhans cell populations to be isolated from epidermal cell suspensions by treatment with anti-class I MHC monoclonal antibody and complement. It is likely that the uniquely low cell-surface expression of class I MHC antigen by Langerhans cells has relevance to both immune responses in the skin as well as to mechanisms of skin allograft rejection. In addition, it is conceivable that regulation of class I MHC expression on antigen-presenting cells in general is an important but hitherto unrecognized mechanism of immune regulation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergstresser P. R., Tigelaar R. E., Dees J. H., Streilein J. W. Thy-1 antigen-bearing dendritic cells populate murine epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Sep;81(3):286–288. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12518332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach S. M., Katz S. I. Keratinocytes synthesize Ia antigen in acute cutaneous graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2741–2745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughman S. W., Breathnach S. M., Sharrow S. O., Stephany D. A., Katz S. I. Culture and characterization of murine dendritic Thy-1+ epidermal cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Jun;86(6):615–624. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12275611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engleman E. G., Warnke R., Fox R. I., Dilley J., Benike C. J., Levy R. Studies of a human T lymphocyte antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1791–1795. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., Singer A. Role of accessory cell processing and presentation of shed H-2 alloantigens in allospecific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):597–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Cooper K. D., Iijima M., Tsuchida T. The role of Langerhans cells in antigen presentation. J Invest Dermatol. 1985 Jul;85(1 Suppl):96s–98s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12275562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata M., Parnes J. R., Herzenberg L. A. Transcriptional control of HLA-A,B,C antigen in human placental cytotrophoblast isolated using trophoblast- and HLA-specific monoclonal antibodies and the fluorescence-activated cell sorter. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):633–651. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F., Nagy Z. A. Genetics of the major histocompatibility complex: the final act. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:119–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Lillehoj E. P., Cowan E. P., Maloy W. L., van Schravendijk M. R., Coligan J. E. Class I genes and molecules: an update. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):3–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuochi T., Golding H., Rosenberg A. S., Glimcher L. H., Malek T. R., Singer A. Both L3T4+ and Lyt-2+ helper T cells initiate cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against allogenic major histocompatibility antigens but not against trinitrophenyl-modified self. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):427–443. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Mayer N., Sachs D. H. Hybridoma cell lines secreting monoclonal antibodies to mouse H-2 and Ia antigens. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romani N., Stingl G., Tschachler E., Witmer M. D., Steinman R. M., Shevach E. M., Schuler G. The Thy-1-bearing cell of murine epidermis. A distinctive leukocyte perhaps related to natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1368–1383. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G. The Langerhans cell. Crit Rev Immunol. 1981 Dec;3(2):95–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler G., Steinman R. M. Murine epidermal Langerhans cells mature into potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells in vitro. J Exp Med. 1985 Mar 1;161(3):526–546. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.3.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal D. M., Stephany D. A. The measurement of specific cell: cell interactions by dual-parameter flow cytometry. Cytometry. 1984 Mar;5(2):169–181. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990050211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrow S. O., Mathieson B. J., Singer A. Cell surface appearance of unexpected host MHC determinants on thymocytes from radiation bone marrow chimeras. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1327–1335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer A., Hathcock K. S., Hodes R. J. Self recognition in allogeneic radiation bone marrow chimeras. A radiation-resistant host element dictates the self specificity and immune response gene phenotype of T-helper cells. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1286–1301. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner G., Wolff K., Pehamberger H., Stingl G. Epidermal cells as accessory cells in the generation of allo-reactive and hapten-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):736–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Kaplan G., Witmer M. D., Cohn Z. A. Identification of a novel cell type in peripheral lymphoid organs of mice. V. Purification of spleen dendritic cells, new surface markers, and maintenance in vitro. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Tamaki K., Katz S. I. Origin and function of epidermal Langerhans cells. Immunol Rev. 1980;53:149–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb01043.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschachler E., Schuler G., Hutterer J., Leibl H., Wolff K., Stingl G. Expression of Thy-1 antigen by murine epidermal cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Sep;81(3):282–285. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12518326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida T., Iijima M., Fujiwara H., Pehamberger H., Shearer G. M., Katz S. I. Epidermal Langerhans cells can function as stimulatory cells but not as accessory cells in CTL induction. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1163–1168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K., Stingl G. The Langerhans cell. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jun;80 (Suppl):17s–21s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]