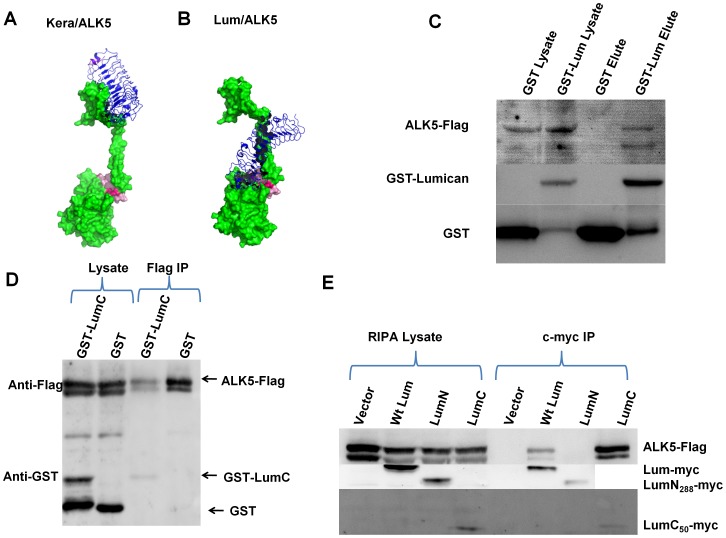
Figure 5. Lumican binds to ALK5: in silico analysis and pull down assays.
In silico molecular dynamic analysis was performed to identify a binding partner of Lum. Panels A and B represent potential binding of Kera and Lum to ALK5 (TGFβ type 1 receptor), respectively. ALK5 in green and the GS domain of ALK5 (TGFbR1) in pink. (A) Keratocan interacts via its Leucine Rich Repeat domain with the extracellular domain of ALK5 with low affinity (ΔG = 30.39 kJ/mol). (B) Lum favorably interacts via its C-terminal domain with the GS domain of ALK5 (ΔG = −100 kJ/mol). The LumC domain has an even higher affinity with ALK5 (ΔG of −1086 kJ/mol). (C) GST pull down assay shows in vitro interaction between ALK5 and GST-Lum. ALK5-Flag was co-eluted with GST-Lum, but not GST, suggesting a direct interaction between Lum and ALK5. (D) In vitro interaction between ALK5 and the C-terminal Lumican. Both ALK5-Flag and GST-LumC were visible in lysates incubated with GST and GST-LumC. IP with an anti-flag antibody resulted in a GST positive band in the mixture of GST-LumC50 and cell lysate, but not in the mixture of GST and lysate, indicating that GST-LumC50, but not GST, is co-precipitated with ALK5-flag by anti-flag antibodies. (E) C-terminal of Lum binds to ALK5. ALK5-Flag was co-precipitated with LumC50-myc and Lum-myc, but not LumN-myc.