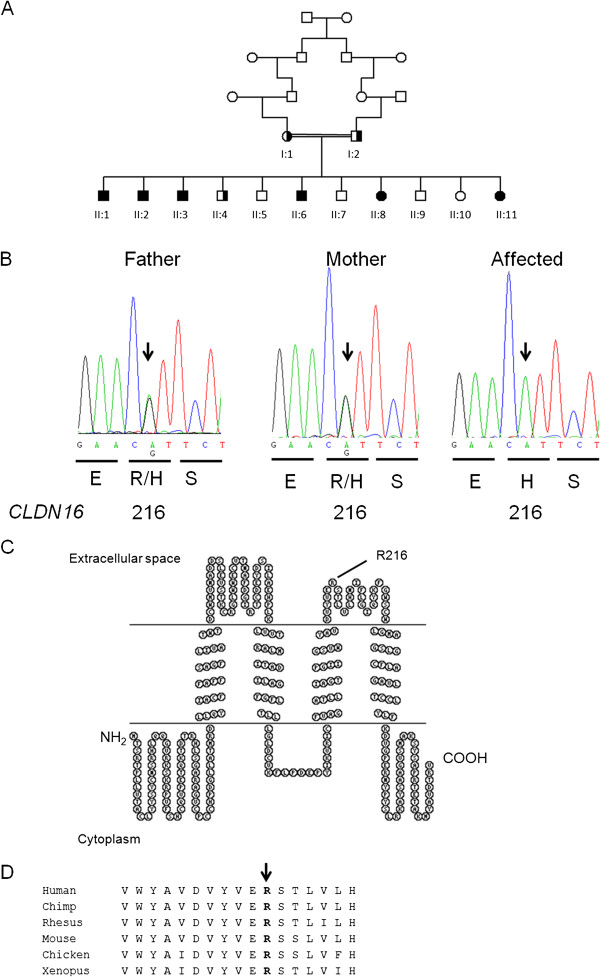
Figure 1.
Molecular genetic investigation of the family. (A) Pedigree diagram of consanguineous multiplex family with homozygous and heterozygously affected members with Familial Hypomagnesaemia with Hypercalciuria and Nephrocalcinosis and CLDN16 mutations. Circles females, squares males, shaded = affected, half shaded = heterozygous carrier. (B) Mutational analysis and segregation demonstrates a c. G647A nucleotide substitution in exon 4 of CLDN16 leading to a missense change p. R216H. Amino acids and position are annotated below the chromatograms. (C) Claudin-16 protein (alias paracellin) model deduced from hydrophobicity plots and drawn using http://www.sacs.ucsf.edu/TOPO2. The mutated R216 in the second extracellular loop is annotated. (D) R216 residue (arrowed) is highly conserved from Human to Xenopus.