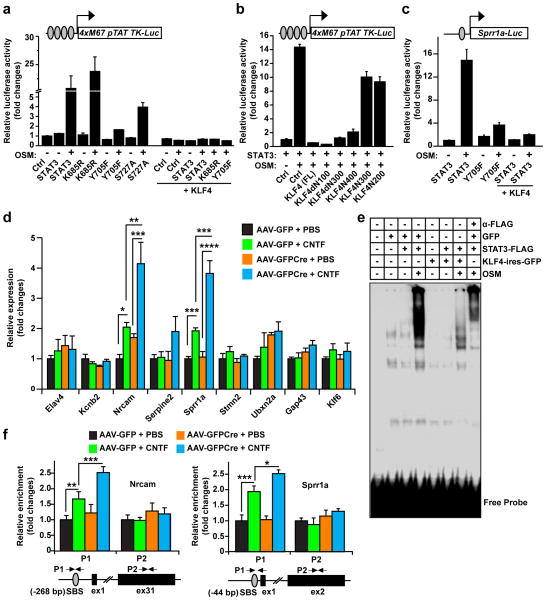
Figure 2. KLF4 inhibits cytokine-induced STAT3 activity.
(a–b) KLF4 suppresses the activity of a STAT3-dependent luciferase reporter in COS7 cells (means ± s.e.m.; n = 3). This reporter contains 4 copies of consensus STAT3-binding sites and requires cytokine-induced phosphorylation of Y705 for its activity. KLF4-truncation mutants that do not bind pSTAT3 lack the ability to suppress this reporter (b). Ctrl: cells transfected with an empty vector as controls. (c) KLF4 inhibits the OSM-induced and STAT3-dependent activity of a reporter from the Sprr1a gene (means ± s.e.m.; n = 3). (d) qRT-PCR analysis showing that KLF4-deletion enhances CNTF-induced gene expression in retinas of Klf4f/f mice (means s.e.m.; n = 3; *p < 0.04, **p < 0.03, ***p < 0.02, and ****p < 0.001 by Student’s t-test). (e) KLF4 disrupts DNA-binding activity of STAT3 detected by EMSA. Nuclear extracts from GFP-transfected COS7 cells were used as controls. The inclusion of an antibody against FLAG-tagged STAT3 leads to a supershift, indicating STAT3-dependent DNA-binding activity. (f) ChIP assays showing that KLF4-deletion enhances CNTF-induced pSTAT3-binding to its target genes in retinas of Klf4f/f mice (means ± s.e.m.; n = 3; *p < 0.04, **p < 0.03, and ***p < 0.02 by Student’s t-test). The positions of primers (P1 or P2) used for qPCR are indicated. SBS, STAT3-binding site; ex, exon.