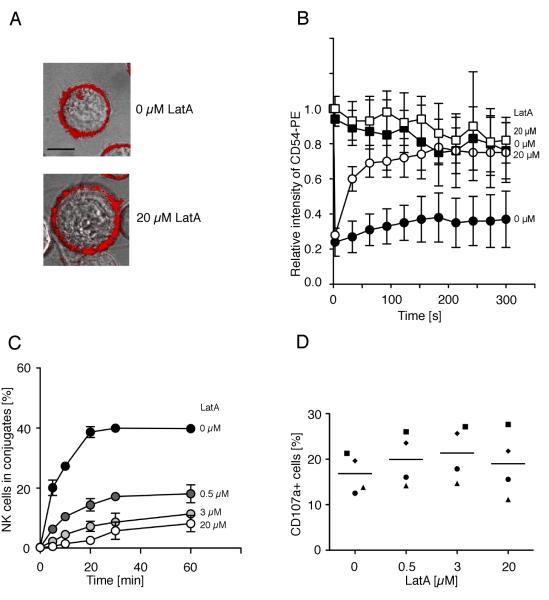
FIGURE 4.
Disruption of actin filaments increases the mobility of ICAM-1 on K562 cells and decreases conjugate formation with NK cells. The mobility of ICAM-1 was determined by FRAP. Cells were stained with a PE-labeled anti-ICAM-1 antibody. Fluorescence recovery in the bleached area of K562 cells either untreated (A, upper panel, bar indicates 5 μm, B, filled circles) or Latrunculin A-treated (A, lower panel, B, open circles) is displayed. Fluorescence intensity of a non-bleached area of the K562 cells either untreated (B, filled squares) or Latrunculin A-treated (B, open squares) served as a control. Bars indicate the SD (untreated cells: n = 9, Latrunculin-A treated cells: n = 6). (C) K562 cells pre-treated with DMSO carrier alone (filled circles), Latrunculin A at indicated concentrations for 40 min at 37°C were tested for conjugate formation with resting NK cells. Bars indicate the SD (n = 3 individual NK cell donors in three independent experiments). (D) K562 target cells treated as in C were mixed with resting NK cells and degranulation was measured after 1 h at 37°C by staining for CD107a at the surface of NK cells. Each symbol indicates one of the four individual NK cell donors. (n = 4 independent experiments).