Fig. 3.
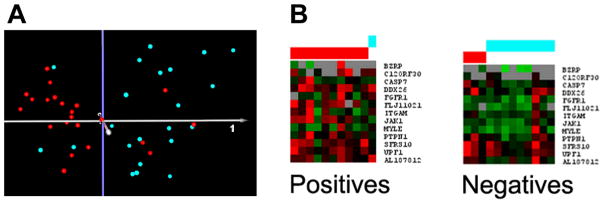
A) Principal components analysis of the qNPA data for cases and controls. Quantitative nuclease protection assays were performed on LCL [22 cases of the severely language-impaired subtype (red) and 22 controls (turquoise)] that were previously analyzed by DNA microarray analyses. Principal components analysis of the qNPA data shows good separation of the samples based on 14 differentially expressed genes, with 72% of the variance represented within the first 3 principal components. B) SVM analysis of the qNPA data for a new set of 13 cases (red) and 10 controls (turquoise). For the SVM analyses, cases were initially identified as positives and controls as negatives for training the classifier.
