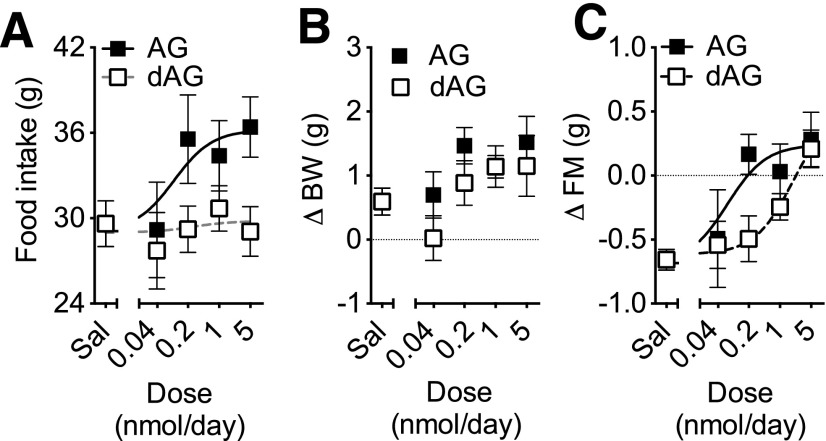
Figure 2.
Effect of chronic intracerebroventricular dAG or AG infusion on food intake, BW, and FM. C57/BL6 mice were given intracerebroventricular infusion of saline, dAG, or AG for 7 days. AG and dAG were infused using increasing doses (0.04, 0.2, 1.0, and 5.0 nmol/day). There was a significant effect of the treatment on 7-day cumulative food intake (P < 0.05 AG vs. dAG, two-way ANOVA). Consistently, a nonlinear regression analysis followed by an extra sum-of-squares F test detected a significant difference between the curves fitting AG and dAG effects (A; P = 0.0185). A two-way ANOVA detected a significant effect of the dose of both AG and dAG on BW (B; P < 0.05) and FM (C; P < 0.001). A nonlinear regression analysis followed by an extra sum-of-squares F test detected a significant difference (P = 0.0318) between the potency of AG and dAG on FM (C). n = 6–10 animals per group. Sal, saline.