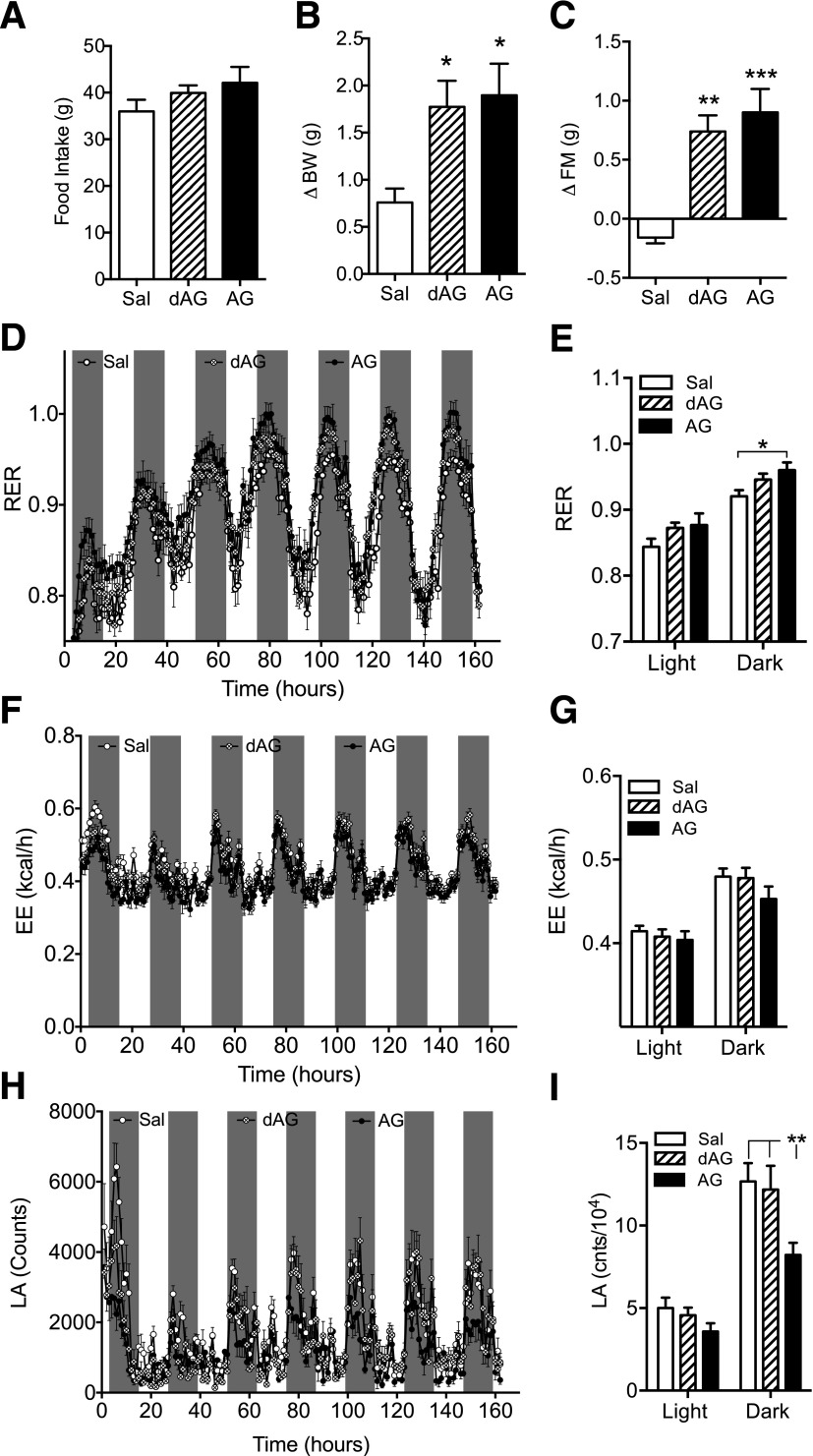
Figure 3.
Effect of chronic intracerebroventricular dAG or AG infusion on RER, EE, and LA. C57BL/6 mice were given intracerebroventricular infusion of saline, dAG, or AG (5 nmol/day) for 7 days while being housed in an indirect calorimetry system. AG and dAG had no effect on 7-day cumulative food intake (A). Both AG and dAG increased BW (B; *P < 0.05 vs. saline, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test) and FM (C; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. saline, one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test). D: Effect of AG and dAG on RER. AG significantly increased RER in the final 4 days of infusion (E; *P < 0.05, AG vs. saline; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). Neither AG nor dAG altered EE throughout the 7-day infusion period (F and G). H: Effect of AG and dAG on LA. Only AG maintained the suppression of LA in the final 4 days of infusion (I; **P < 0.01, AG vs. saline; two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test). n = 7–8 animals per group. Sal, saline.