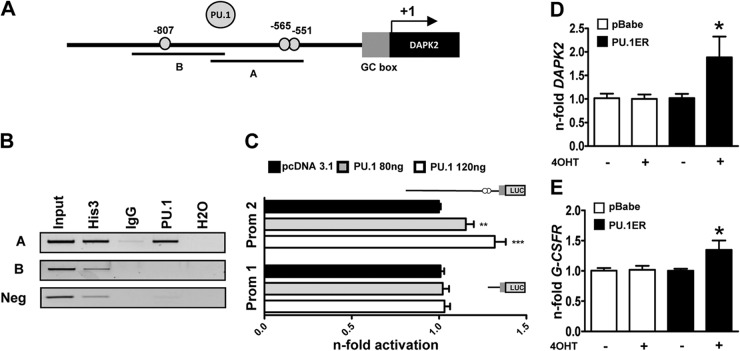
Figure 3. PU.1 is a transcriptional regulator of DAPK2 during neutrophil differentiation.
(A) Schematic representation of putative PU.1-binding sites in the proximal DAPK2 promoter. (B) PU.1 ChIP assays using NB4 cells. Histone 3 and IgG served as positive and negative controls, respectively. PCR was performed using primers encompassing the −807 or the −565 and the −551 PU.1-binding site in the DAPK2 promoter and an unrelated sequence 1.6 kb downstream of the GC box which served as a negative control. (C) PU.1 activates the DAPK2 promoter (Prom 1/2). Transactivation assays of H1299 cells transiently transfected with PU.1 expression or pcDNA3.1 empty vector together with a long or short DAPK2 promoter reporter construct as indicated. The promoter activity is shown as relative light units and was normalized to pcDNA3.1-transfected cells. (D) Induction of ectopic PU.1 increases DAPK2 mRNA levels. NB4 cells were transduced with an inducible PU1-ER-expressing vector. Cells were treated with 4-OHT to induce PU.1 translocation to the nucleus. DAPK2 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR, and values were normalized to the HMBS housekeeping gene. Results are given as n-fold regulation compared with untreated, control-transduced NB4 pBabe cells. (E) Induction of G-CSFR mRNA is shown as a control for PU.1 transcriptional activity. Analysis as in D. MWU: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.