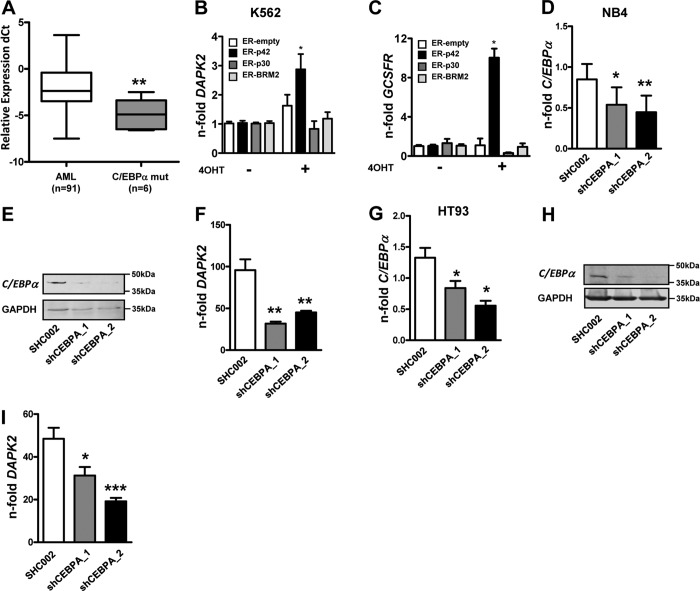
Figure 6. DAPK2 levels correlate with C/EBPα inactivation in AML.
(A) Down-regulation of DAPK2 mRNA levels in C/EBPα-mutated (CEBPA mut) AML patients. DAPK2 mRNA levels in AML blast cells were quantified using qPCR. Values are the differences in Ct values between DAPK2 and the housekeeping genes ABL1 and GAPDH. (B) K562 leukemic cells expressing inducible WT C/EBPα (p42), the N-terminus truncated form (p30), or the C-terminus mutated form (BRM2) were treated with 5μM 4-OHT to induce the translocation of the C/EBPα-ER proteins to the nucleus. Activation of WT but not the truncated C/EBPα proteins resulted in a significant increase of DAPK2 mRNA levels. (C) Induction of the C/EBPα target gene G-CSFR is shown as a control for C/EBPα transcriptional activity. (D and E) NB4 APL cells were transduced with two independent shRNAs (shC/EBPα_1/_2) targeting C/EBPα and differentiated for 4 days using ATRA. C/EBPα knockdown efficiency was analyzed by qPCR and Western blotting. Transcript values were normalized to the housekeeping gene HMBS and are given as n-fold regulation compared with ATRA-treated control cells. Total protein was extracted and subjected to immunoblotting using anti-C/EBPα antibody. GAPDH is shown as a loading control. (F) Knocking down C/EBPα results in significantly decreased induction of DAPK2 message upon neutrophil differentiation of NB4 cells. Analysis as in C. (G and H) HT93 APL cells were transduced with two independent shRNAs (shC/EBPα_1/_2) targeting C/EBPα. Treatment and C/EBPΑ mRNA measurements were done as in D and E. (I) Knocking down C/EBPα results in significantly decreased induction of DAPK2 message upon neutrophil differentiation of HT93 APL cells. Treatment and analysis as in C. MWU: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.