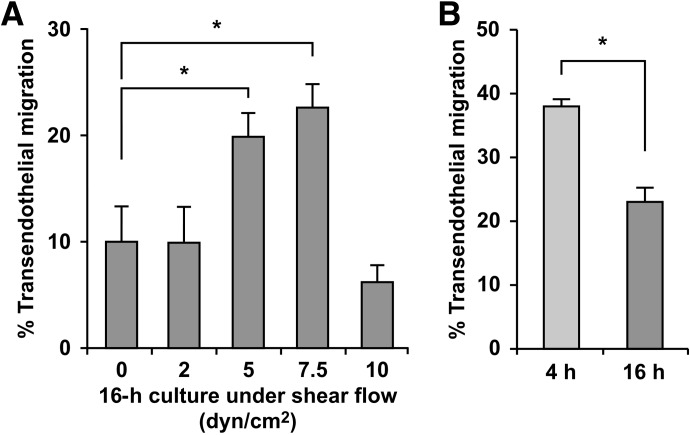
Figure 3. Application of shear flow during ex vivo incubation leads to less impairment of monocyte transendothelial migration than static incubation.
To maintain monocytes under conditions during ex vivo incubation that more closely mimic those in the circulation, shear flow was introduced by shaking the freshly prepared monocytes in polypropylene tubes with a rotary shaker. (A) Monocytes were shaken for 16 h at various speeds to attain fluid flow conditions that are estimated as shear stresses of 2, 5, 7.5, and 10 dyn/cm2, and their frequencies of diapedesis on TNF-activated HUVEC monolayers were evaluated by 2-h time-lapse microscopy, as described in Fig. 1. Means ± sem from experiments using four different monocyte donors for 5 dyn/cm2, and three for other conditions are shown; *P < 0.05 (unpaired t-test). (B) Monocytes were isolated from individual donors and shaken separately at 7.5 dyn/cm2 for 4 and 16 h (fourth column of Fig. 3A), and the frequencies of diapedesis were evaluated immediately after the incubation and then compared. Means ± sem from independent experiments using three different monocyte donors are shown; *P < 0.05 (paired t-test).