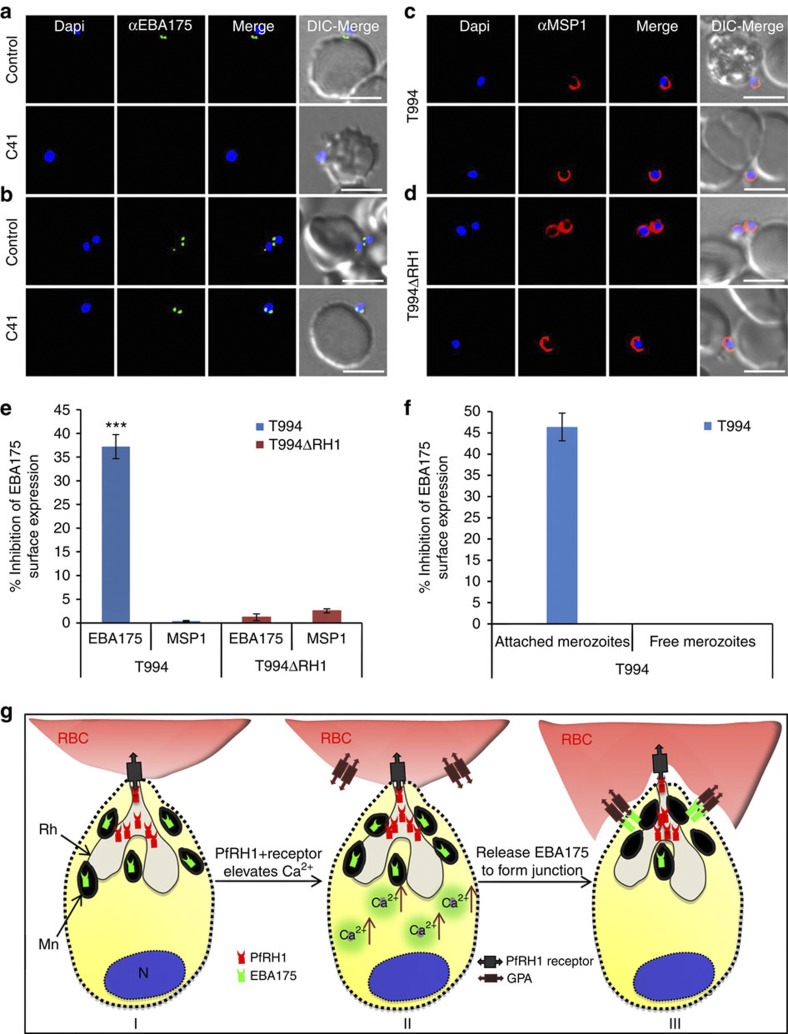
Figure 6. Effect of anti-PfRH1 inhibitory mAbs on merozoite surface expression of EBA175 during invasion.
(a–d) Surface expression of EBA175 and MSP1 on T994 and T994ΔRH1 was detected by immunofluorescence assays. Isolated T994 (a,c) or T994ΔRH1 (b,d) merozoites were directly incubated with erythrocytes containing 4 μM Cyto D in the absence (Control) and presence (C41) of C41 (0.2 mg ml−1) before analysis of expression of EBA175 and MSP1 at the junction. Both differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence images were captured. Nuclear DNA was counterstained with DAPI (blue). EBA175 is shown in green, whereas MSP1 is shown in red. Fluorescence images, merged fluorescence images (DAPI and green or DAPI with red) and merged fluorescence images with DIC images are shown. Scale bars=10 μM. (e) EBA175 surface expression on merozoites was detected by using a fluorescence plate reader. Surface expression of EBA175 and MSP1 on merozoite in the presence of C41 was compared with their controls. Experimental data are presented as the mean±s.e.m.; n=3. ***P≤0.000025 by one-way ANOVA, indicating that C41 significantly decreases the surface expression of EBA175 in T994. (f) T994 merozoite EBA175 surface expression was also detected by flow cytometry during invasion (detail shown in Supplementary Fig. S8). Statistical analysis of the effect of C41 on merozoite EBA175 surface expression is shown. Merozoite attached to RBCs surface expression of EBA175 in the presence of C41 was compared with its positive control. Experimental data are presented as the mean±s.e.m.; n=4. (g) Schematic diagram of Ca2+ signalling in junction formation during erythrocyte invasion. After the merozoite initially attaches to the erythrocyte (RBC) and reorients itself, PfRH1 released from rhoptry (Rh) is responsible for sensing the apical end interaction (I). The binding of PfRH1 to its receptor triggers an increase of intracellular Ca2+ (II). Rise in cytosolic Ca2+ levels results in release of microneme (Mn) proteins such as EBA175 to bind to glycophorin A (GPA), which leads to tight junction formation (III).