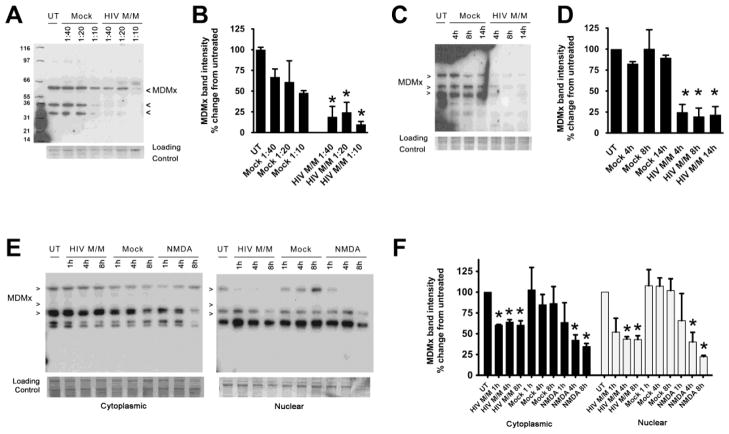
Figure 2. HIV M/M leads to decreases in MDMx in a time- and dose-dependent manner.
A – D. Primary neuroglial cultures that were 21 days in vitro (DIV) were treated with mock-infected macrophage supernatants (Mock) or HIV-infected macrophage supernatants (HIV M/M) at the indicated doses for 20 hours. Western immunoblotting of whole cell protein lysates shows a dose-dependent (A, B) and a time-dependent (C, D) decrease in MDMx levels (n=4, One-way ANOVA, post-hoc Newman-Keuls, * p<0.05 vs. untreated). E–F. Cytoplasmic and nuclear extracts from primary neuroglial cultures treated with either Mock (1:20 dilution), HIV M/M (1:20 dilution) or NMDA (10 μM) for 1, 4, or 8 hours were immunoblotted for MDMx. HIV M/M treatment led to statistically significant decreases in MDMx protein levels in both cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions. Likewise, NMDA treatments led to significant decreases in nuclear MDMx levels starting at 4 hour following treatment (n=3, One-way ANOVA, post-hoc Newman-Keuls, * p<0.05 vs. untreated). Mock did not cause a change in MDMx levels in either cytoplasmic or nuclear fractions. Representative immunoblots of at least three biological replicates are shown. Note that the antibody used against MDMx detects at least three isoforms in protein lysates.