Abstract
We have reported previously that the incidence of tumors induced in Sprague-Dawley rats by total-body gamma-ray irradiation can be considerably reduced by restriction of food intake [Gross, L. & Dreyfuss, Y. (1984) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 7596-7598]. In experiments reported here we investigated the influence of reduced food intake on the development of radiation-induced leukemia in C3H(f) mice. The incidence of spontaneous leukemia in mice of this strain does not exceed 0.5%, but it can be considerably increased by total-body x-irradiation. In our study, two groups of C3H(f) mice were submitted to fractionated total-body gamma-irradiation (150 rads, five times at weekly intervals; 1 rad = 0.01 gray). The first group received a full ad lib diet (4.5-5.4 g of Purina Rodent Lab Chow pellets per day, each). In this group 31 out of 58 females (53.4%) and 24 out of 50 males (48%) developed leukemia at an average age of 8 months. In the second group, consisting of sisters and brothers of the first group, and submitted to the same gamma-irradiation but receiving a restricted diet (2 g of Purina Lab Chow pellets each, followed by 3 g on alternate days), only 2 out of 55 females (3.6%), and 1 out of 36 males (2.8%), developed leukemia at an average age of 9 and 12 months, respectively. Leukemia in both groups was predominantly of the lymphatic or lymphoblastic form, the leukemic cells infiltrating most organs, particularly the thymus, mesenteric and peripheral lymph nodes, spleen, liver, kidneys, and bone marrow; in most instances the peripheral blood was also leukemic.
Full text
PDF

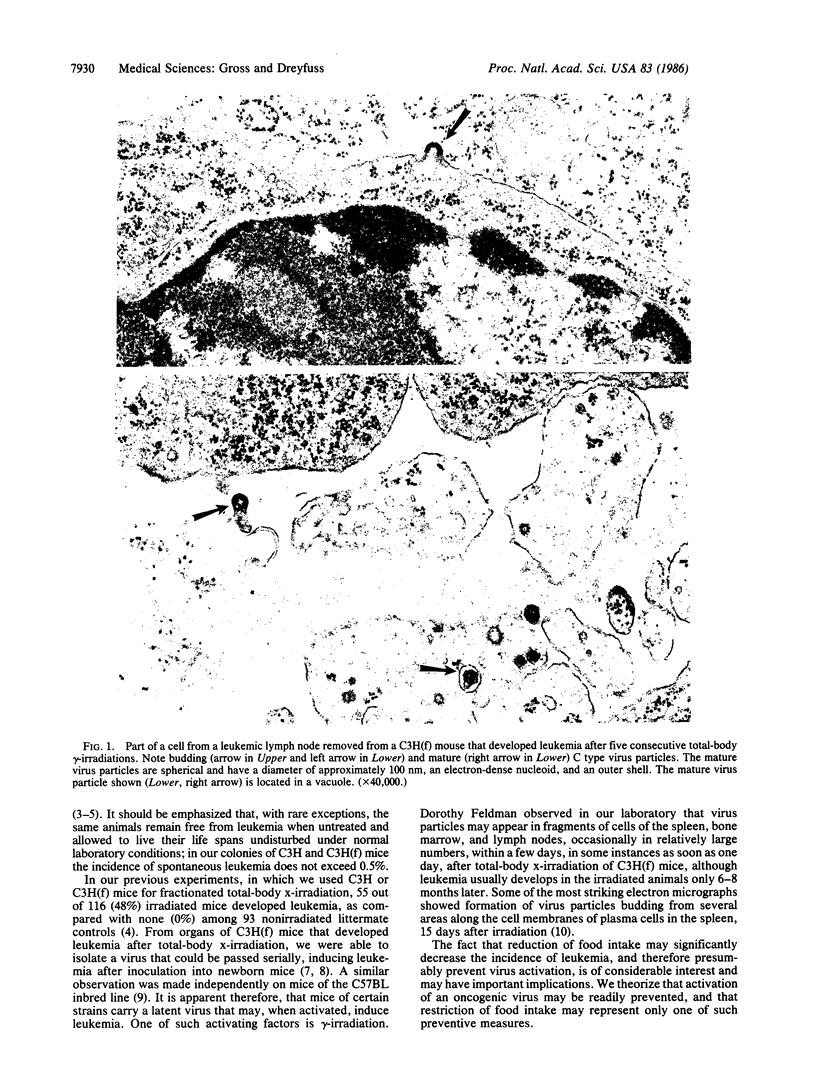

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GROSS L. Attempt to recover filterable agent from x-ray induced leukemia. Acta Haematol. 1958 Jun;19(6):353–361. doi: 10.1159/000205455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS L., ROSWIT B., MADA E. R., DREYFUSS Y., MOORE L. A. Studies on radiation-induced leukemia in mice. Cancer Res. 1959 Apr;19(3 Pt 1):316–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS L. [Serial cell-free passage of a radiation-activated mouse leukemia agent]. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Jan;100(1):102–105. doi: 10.3181/00379727-100-24538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross L., Dreyfuss Y. Reduction in the incidence of radiation-induced tumors in rats after restriction of food intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7596–7598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross L., Dreyfuss Y. Spontaneous tumors in Sprague-Dawley and Long-Evans rats and in their F1 hybrids: carcinogenic effect of total-body x-irradiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5910–5913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross L., Feldman D. G. Electron microscopic studies of radiation-induced leukemia in mice: virus release following total-body x-ray irradiation. Cancer Res. 1968 Sep;28(9):1677–1685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN H. S., BROWN M. B. A quantitative dose-response study of lymphoid-tumor development in irradiated C 57 black mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1952 Aug;13(1):185–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN M., KAPLAN H. S. Leukemogenic activity of filtrates from radiation-induced lymphoid tumors of mice. Science. 1959 Aug 14;130(3372):387–388. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3372.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew E. A., Garfinkel L. Variations in mortality by weight among 750,000 men and women. J Chronic Dis. 1979;32(8):563–576. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(79)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




