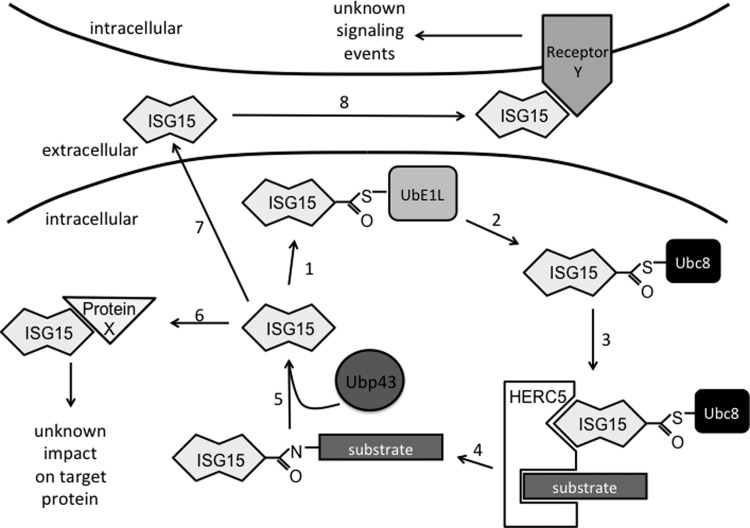
FIG. 1.
Schematic of the 3 forms of ISG15. The IFN-induced E1/E2/E3 enzymatic cascade catalyzes ISGylation of substrate proteins. The activating E1 enzyme UbE1L forms a thioester bond with free ISG15 in an ATP-dependent manner (1). ISG15 is then transferred to the E2 conjugating enzyme Ubc8 (2). Interaction with the E3 ligase HERC5 (3) then catalyzes the conjugation of ISG15 to lysine residues of target substrate proteins (4). The deconjugating enzyme Ubp43 reverses conjugation by removing ISG15 from target proteins (5). Free intracellular ISG15 may bind noncovalently to unknown intracellular proteins (6) and impact downstream signaling. Secretion of free intracellular ISG15 (7) results in extracellular ISG15 that may bind to its unknown receptor(s) (8) to initiate unknown signaling pathways. IFN, interferon; ISG, IFN-stimulated gene.