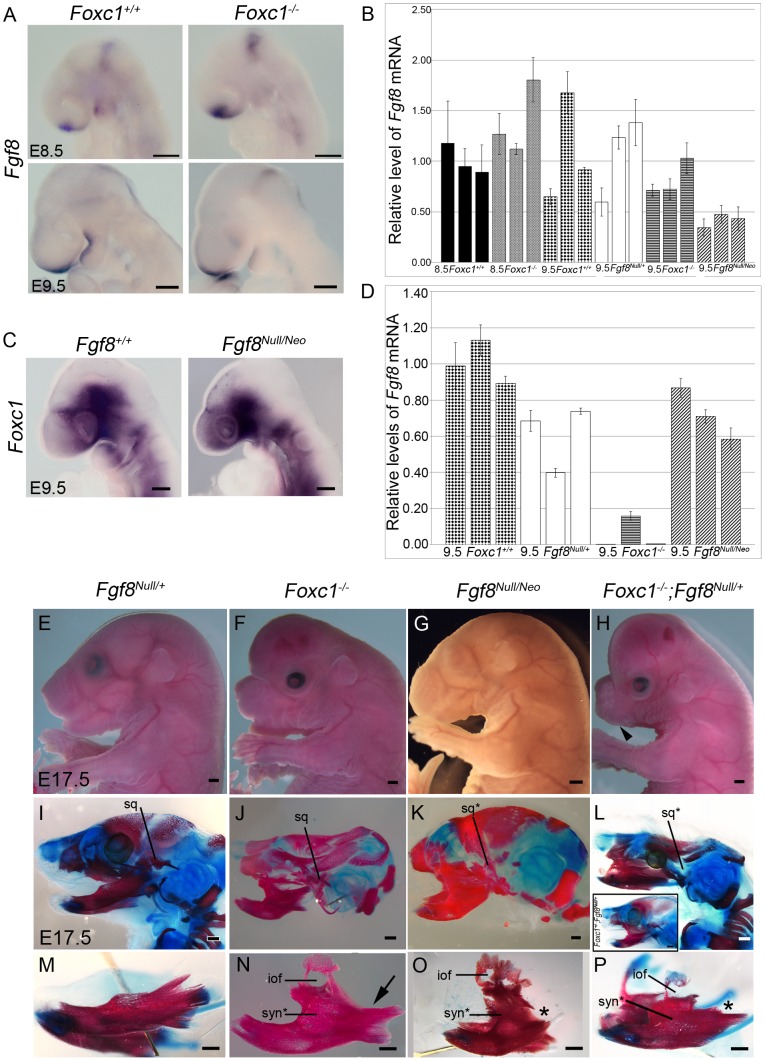
Figure 7. Foxc1 is required to maintain Fgf8 signaling and genetically interacts with Fgf8.
(A) Fgf8 expression is maintained in the frontonasal prominence and midbrain-hindbrain boundary regions of Foxc1−/− embryos, but it is reduced in the PA1 oral ectoderm (red asterisks). (B) Quantification of Fgf8 mRNA in Foxc1, Fgf8Null/+, and Fgf8Null/Neo embryos. (C) Foxc1 is normally localized in Fgf8Null/Neo embryos. (D) Quantification of Foxc1 mRNA in Foxc1, Fgf8Null/+, and Fgf8Null/Neo embryos. Gross appearance (E–H) and skeletal preparations (I–P) of E17.5 embryos comparing Fgf8Null/+ (E, I, M), Foxc1−/− (F, J, N), Fgf8Null/Neo (G, K, O), Foxc1+/−; Fgf8Null/+ (L, inset), and Foxc1−/−;Fgf8Null/+ (H, L, P) phenotypes. In both gross view (E) and skeletal preparations (I, M), Fgf8Null/+ are indistinguishable from wild-type embryos. (F) Foxc1−/− embryos have shortened frontonasal regions, open eyelids, abnormal and shifted external ears, and enlarged, hydrocephalic cerebral hemispheres. (G) Fgf8Null/Neo embryos have a more rounded frontonasal region, small lower jaw, and abnormal, shifted external ears. (H) Compound Foxc1−/−;Fgf8Null/+ embryos resemble Foxc1−/− specimens, but have more severe frontonasal shortening and no externally visible oral opening/lower jaw (black arrowhead). (J, N) Hypoplastic squamosal (sq), syngnathia (syn*), and abnormal condyle formation in the absence of Foxc1. This specimen shows fusion in alveolar region of dentary and absence of the coronoid process (arrow in N). (K, O) Severe hypoplasia and malformation of the squamosal (sq*) was observed in FgfNull/Neo specimens. The frontal process of the maxilla with a characteristic infraorbital foramen (iof) formed, and the maxilla fused to the dentary in the alveolar region, more distally than seen in Foxc1−/−. The proximal processes of the dentary are absent (asterisk in O), but distal incisors form. (L, P) In Foxc1−/−;Fgf8Null/+ embryos, the syngnathic phenotype is further exacerbated. No squamosal formed and a small frontal process of the maxilla is attached to the hypoplastic maxilla. This region is fused to the dentary just proximal to the lower incisors resulting in flattening of the normally curved dentary. The proximal dentary is severely truncated and lacks all processes (asterisk in P). (inset in L) Foxc1+/−;Fgf8Null/+ compound heterozygote (2/12) in which calvaria had developed normally. This specimen also displayed a syngnathic jaw with TMJ abnormalities grossly identical to that of the Foxc1 null. Scale bars: (A,C) 200 µm; (G–H) 1000 µm; (M–P) 500 µm.