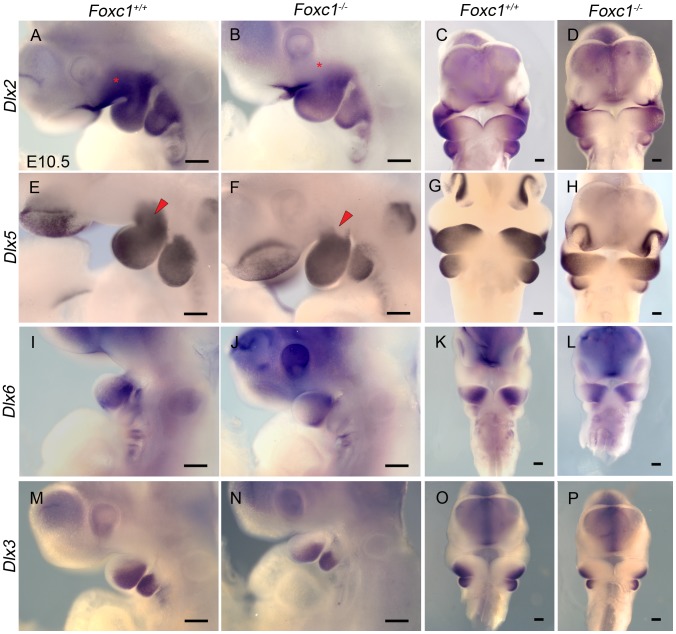
Figure 8. Disruption of proximal Dlx code in PA1 of Foxc1−/− embryos.
Whole mount in situ hybridization in E10.5 Foxc1+/+ (A, C, E, G, I, K, M, O) and Foxc1−/− (B, D, F, H, J, L, N, P) embryos. Lateral (A, B, E, F, I, J, M, N) and frontal (C, D, G, H, K, L, O, P) views are shown for each probe. (A–D) Dlx2 expression is maintained in the λ-junction and distal mandibular ectoderm and the mandibular mesenchyme of Foxc1−/− embryos. However, expression of Dlx2 is much reduced in the maxillary PA1 mesenchyme in the mutants (red asterisks). (E–H) Dlx5 expression is maintained in nasal prominence epithelia, distal mandibular ectoderm, and most of the mandibular mesenchyme in Foxc1−/− embryos. A discrete domain of mesenchymal Dlx5 expression is lost at the Mx-Md junction (red arrowheads) in the absence of Foxc1. In Foxc1−/− both Dlx6 (I–L) and Dlx3 (M–P) are expressed similarly to controls. Scale bars: 200 µm.