Figure 1. The role of CHOP in HCC pathogenesis.
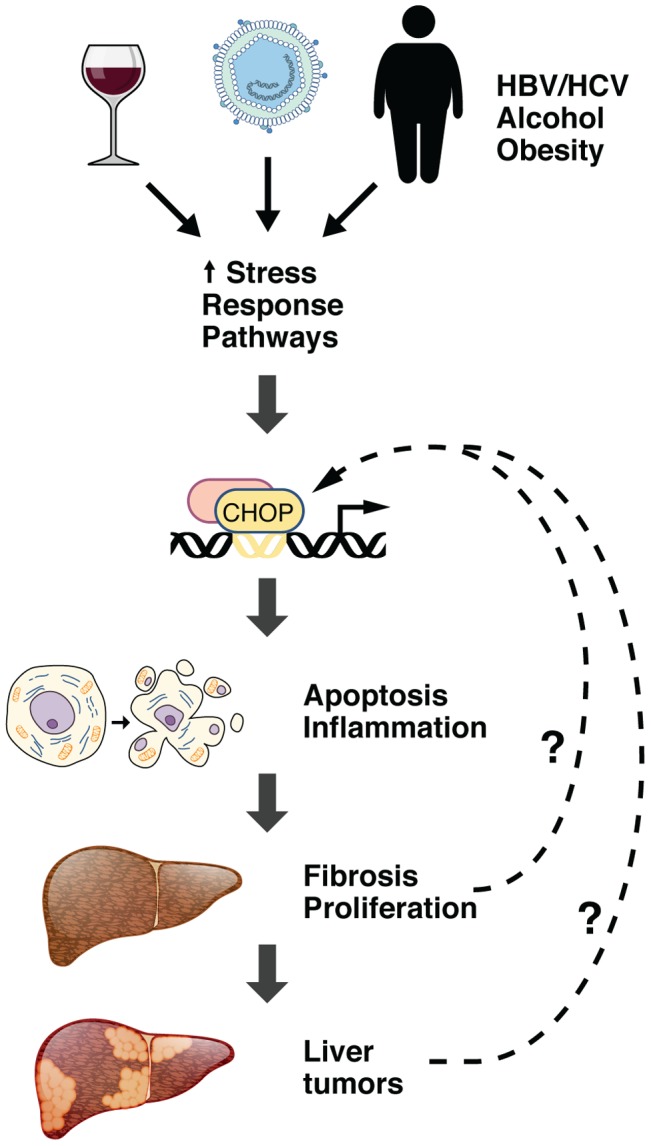
Hepatocyte injury, including toxicity from viral hepatitis, obesity, or alcoholism, promotes the induction of canonical ER stress pathways, including the UPR and ISR. This results in induction of the CHOP transcription factor, which stimulates cell death and provokes an inflammatory response. Inflammation may further stimulate fibrosis and compensatory proliferation, leading to the development of liver tumor nodules. It is also possible that stress caused by fibrosis and proliferation of dysplastic hepatocytes in HCC may induce expression of CHOP, further amplifying its effect on tumorigenesis.
