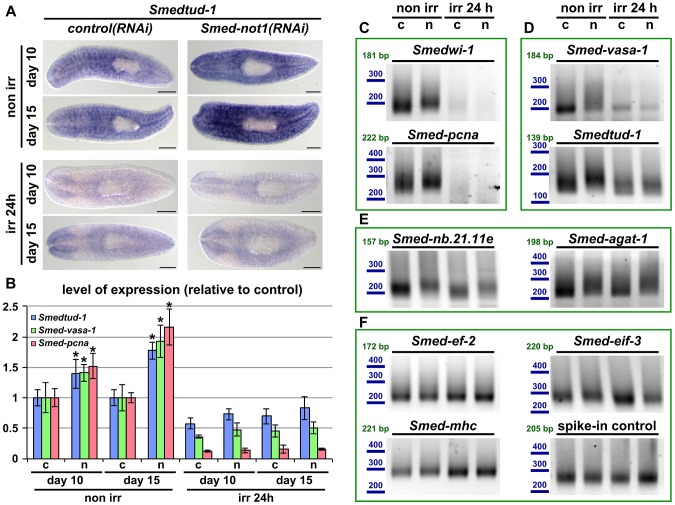
Figure 7. Increased levels of neoblast transcripts and their increased frequency of long poly(A) tails are irradiation sensitive.
(A) WMISH of the neoblast marker Smedtud-1 in control(RNAi) animals (left panels) and Smed-not1(RNAi) animals (right panels) non irradiated (top panels) and irradiated 24 hours (bottom panels) prior to data collection time points 10 and 15 days after RNAi. A consistent qualitative difference is observed in non irradiated animals, however, no qualitative differences are observed in irradiated animals, showing that Smed-not1(RNAi) animals do not overexpress ectopically Smedtud-1. Anterior is to the left. Scale bars: 500 µm. (B) Quantification of the level of expression by qRT-PCR of the neoblast markers Smedtud-1, Smed-vasa-1 and Smed-pcna in control(RNAi) (c) and Smed-not1(RNAi) (n) animals non-irradiated and irradiated 24 hours prior to data collection time points 10 and 15 days after RNAi, normalized expression and relative to respective control(RNAi) samples. Error bars represent standard deviation, asterisks represent statistical significance. Smedtud-1, Smed-vasa-1 and Smed-pcna transcripts accumulate progressively after 10 and 15 days of RNAi, but this accumulation is eliminated 24 hours post irradiation, with Smed-not1(RNAi) irradiated animals showing levels similar to control(RNAi) irradiated animals. (C–F) PAT assays reflecting the distribution of mRNA poly(A) tail lengths for the neoblast specific mRNAs Smedwi-1 and Smed-pcna (C), the neoblast and CNS expressed mRNAs Smed-vasa-1 and Smedtud-1 (D), the progeny specific mRNA Smed-nb.21.11e and Smed-agat-1 (E) and the housekeeping and tissue specific mRNAs Smed-ef-2, Smed-eif-3, Smed-mhc and a spiked-in control in control(RNAi) (c) and Smed-not1(RNAi) (n) animals non irradiated and irradiated 24 hours prior to data collection time points 15 days after RNAi. Size markers used are represented in blue, the theoretical length of the amplicon corresponding to the deadenylated mRNA species given the primers used in each assay is given in green. Neoblast specific markers are not detected after irradiation (C). The marked differences in poly(A) tail length distribution detected for the neoblast and CNS mRNAs Smed-vasa-1 and Smedtud-1 are eliminated by irradiation, showing that the fractions of these mRNA populations localised in the CNS show no differences after Smed-not1 knock down (D). The differences in poly(A) tail length distribution detected for the progeny specific mRNAs Smed-nb.21.11e and Smed-agat-1 are not affected by irradiation, as these cells are not eliminated after 24 hours of irradiation (E). No differences are detected for Smed-ef-2, Smed-eif-3, Smed-mhc and a spike-in control RNA.