Figure 8. Increased level of transcripts and increased frequency of long poly(A) tails are restricted to neoblast-containing cell populations.
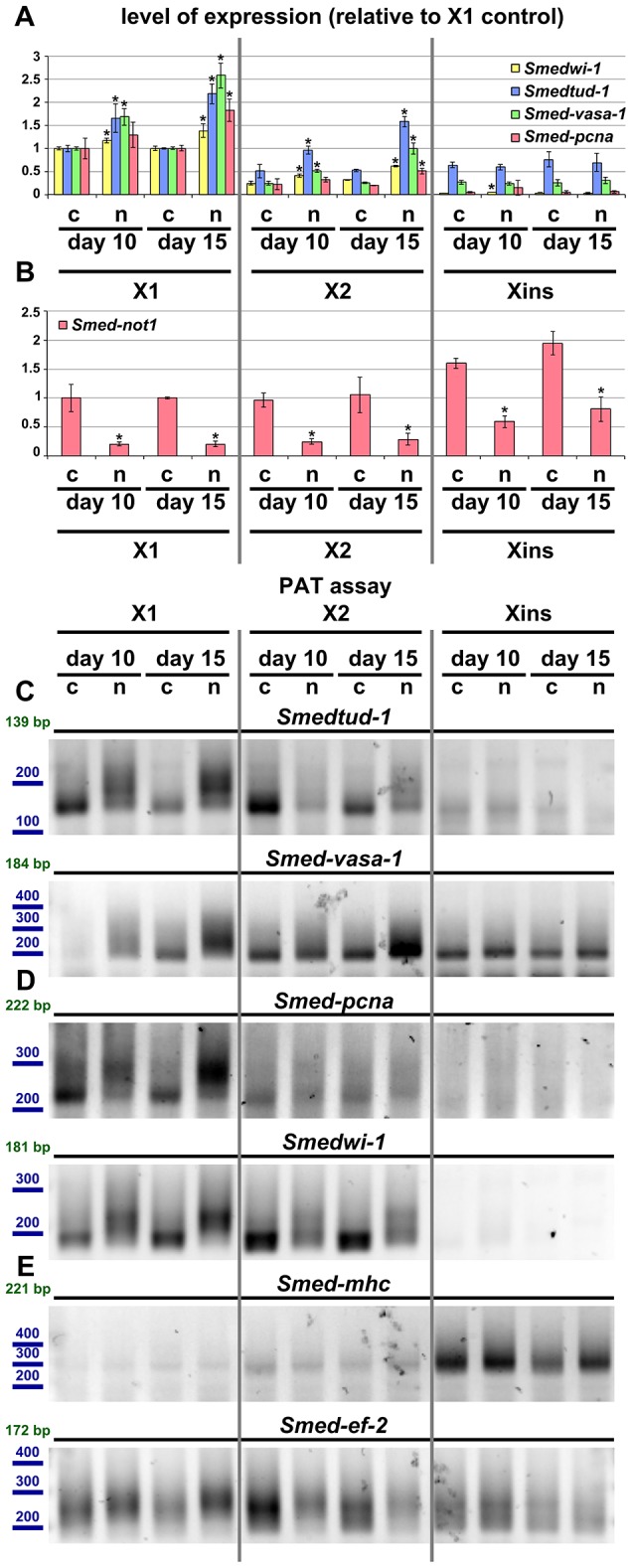
(A–B) Quantification of the level of expression by qRT-PCR of the neoblast markers Smedwi-1, Smedtud-1, Smed-vasa-1 and Smed-pcna (A) and Smed-not1 (B) in FACS sorted populations X1, X2 and Xins in control(RNAi) (c) and Smed-not1(RNAi) (n) animals 10 and 15 days after RNAi, normalized expression and relative to respective X1 control(RNAi) samples. (A) Smedwi-1, Smedtud-1, Smed-vasa-1 and Smed-pcna transcripts accumulate progressively after 10 and 15 days of RNAi in X1 and X2 cells, the two fractions that contain neoblasts to different extents, but this accumulation is not observed in Xins cells, which contain differentiated cells exclusively, including CNS cells. (B) Smed-not1 is significantly depleted across all three cell fractions, showing that the absence of accumulation and increased frequency of long poly(A) tails of neoblast mRNAs that are expressed also in CNS is not due to absence of effective gene knock down in differentiated cells. Error bars represent standard deviation and asterisks represent statistical significance in A–B (C–E) PAT assays reflecting the distribution of mRNA poly(A) tail lengths for the neoblast and CNS expressed mRNAs Smedtud-1 and Smed-vasa-1 (C), the neoblast specific mRNAs Smed-pcna and Smedwi-1 (D) and the housekeeping and tissue specific mRNAs Smed-mhc and Smed-ef-2 (E) in FACS sorted populations X1, X2 and Xins from control(RNAi) (c) and Smed-not1(RNAi) (n) animals 10 and 15 days after RNAi. Size markers used are represented in blue, the theoretical length of the amplicon corresponding to the deadenylated mRNA species given the primers used in each assay is given in green. (C). The marked differences in poly(A) tail length distribution detected for the neoblast and CNS mRNAs Smed-vasa-1 and Smedtud-1 are only detected in X1 and X2 but not in Xins FACS sorted populations, showing that the fractions of these mRNA populations localised in the CNS show no differences after Smed-not1 knock down. (D) The marked differences in poly(A) tail length distribution detected for the neoblast specific mRNAs Smed-pcna and Smedwi-1 are only detected in X1 and X2 but the mRNAs are not detected in Xins FACS sorted populations. (E) No differences in poly(A) tail length distribution are detected for the tissue specific mRNA Smed-mhc, and only slight differences are detected in X1 and X2 but not in Xins fractions for the housekeeping mRNA Smed-ef-2.
