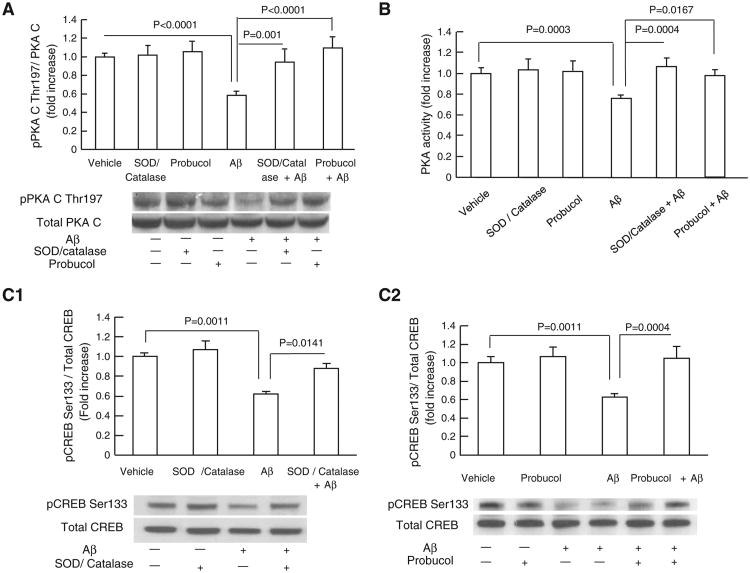
Fig. 1.
Antioxidants attenuated Aβ-induced inhibitory effects on pPKA C and pCREB levels. (A) The treatment of SOD (200 U/ml)/catalase (250 U/ml) or probucol (10 μM) significantly attenuated Aβ (5 μM, 2 h)-induced decrease in pPKA C level. Densitometry of the pPKA C immunoreactive bands relative to the total PKA C was shown in the indicated groups of cells. The lower panel showed representative immunoblots for pPKA C and total PKA C in the indicated groups. (B) The treatment of antioxidants attenuated Aβ-induced reduction in PKA activity. (C1–C2) Densitometry of the immunoreactive bands for phospho-CREB (pCREB) relative to the total CREB in the indicated groups of cells. Levels of pCREB were increased in cells treated with SOD/catalase (C1) and probucol (C2) in the presence of Aβ. The lower panels in C1 and C2 showed the representative immunoblots for pCREB and total of CREB. Results were derived from 3 to 5 independent experiments.