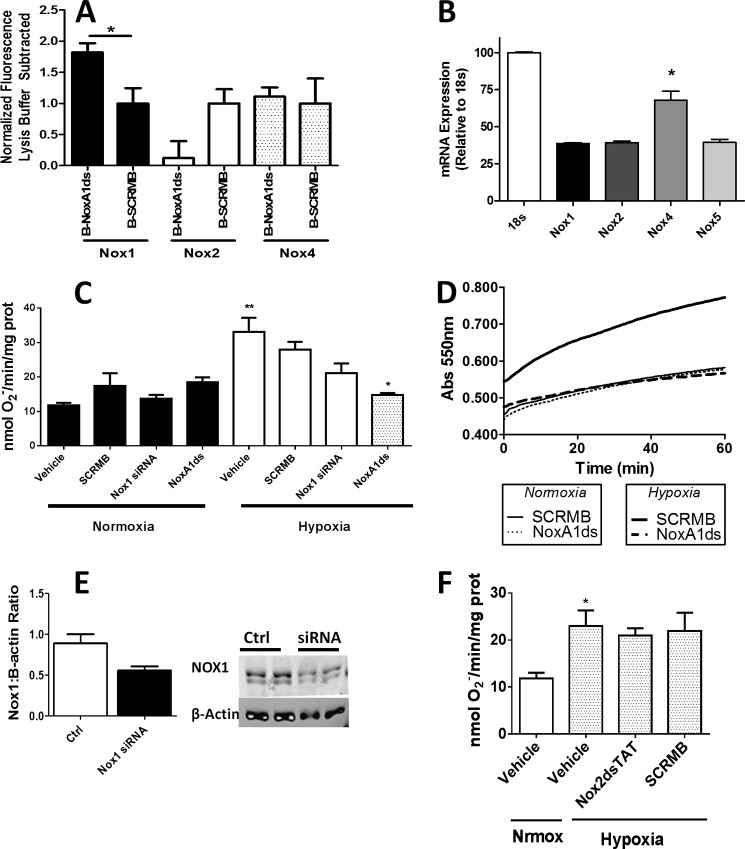
FIGURE 5.
NoxA1ds attenuates hypoxia-induced O2⨪ production. A, NoxA1ds binds to Nox1 but not Nox2 or Nox4 in HPAEC. Neutravidin-coated plates were incubated with biotin-tagged NoxA1ds (B-NoxA1ds) or biotin-tagged SCRMB (B-SCRMB) before addition of HPAEC cell membranes. Captured Noxes were detected through a Alexa 488-conjugated secondary antibody bound to the Nox1, -2, or -4 primary antibody. Fluorescence was expressed with background lysis buffer fluorescence subtracted. When fluorescence was detected via Nox1 primary antibody, there was a significant increase in binding as compared with B-SCRMB. n = 4, *, p < 0.05, unpaired t test. B, relative Nox expression in HPAEC quantified by quantitative PCR. C, in hypoxia and normoxia, SCRMB and NoxA1ds peptides were added to cells at 10 μm for 1 h prior to cell lysis and quantification of enzyme activity. Cells were transfected with Nox1 siRNA 24 h prior to 24-h normoxic/hypoxic treatment followed by cell lysis and quantification of enzyme activity. SCRMB, NoxA1ds, and Nox1 siRNA had a negligible effect on O2⨪ production under normoxic conditions. Hypoxia (1.0% O2, 24 h) treatment resulted in a 3-fold increase in O2⨪ production that was unaffected by SCRMB. Upon treatment with NoxA1ds, O2⨪ production by cells subjected to hypoxia returned to the amount observed under normoxia. D, representative experimental trace for enzyme activity in B shown as the SOD-inhibitable reduction of cytochrome c over time. n = 9, three separate experiments. E, Western blot analysis of Nox1/β-actin protein from Nox1 siRNA or control-treated HPAEC. Nox1 knockdown was incomplete and approximates the degree of knockdown observed as O2⨪ production. F, hypoxia (1.0% O2, 24 h) treatment resulted in a 2-fold increase in HPAEC O2⨪ production that was unaffected by Nox2dsTAT or its control (SCRMB). n = 9, three separate experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test.