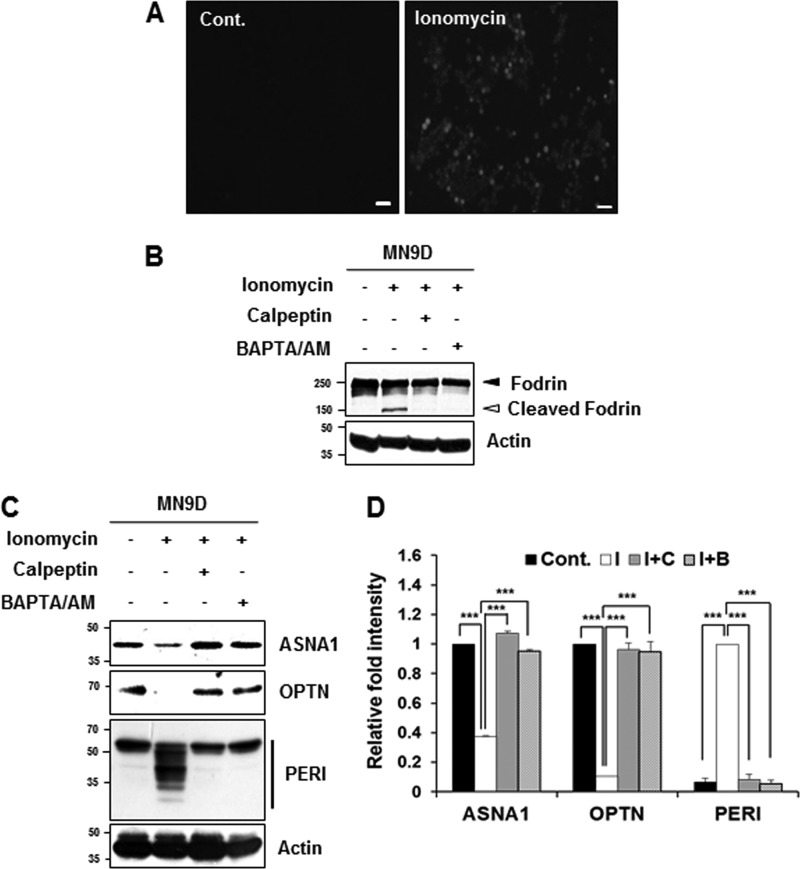
FIGURE 5.
Cleavage of the identified substrates during ionomycin-induced cell death. A, MN9D cells were incubated with or without ionomycin (5 μg/ml) for 30 min. After incubation, cells were stained with 3 μm Fluo-3/AM dye and examined under a fluorescence microscope equipped with epifluorescence filters and a digital analyzer. Scale bars represent 50 μm. B, MN9D cells were incubated for 30 min with ionomycin (5 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of calpeptin (50 μm) or BAPTA/AM (40 μm). After incubation, cellular lysates (50 μg) from each condition were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. Ionomycin-induced calpain activation was confirmed with the anti-fodrin antibody. Actin was used as a loading control. C, MN9D cells were incubated for 30 min at 37 °C with ionomycin (5 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of 50 μm calpeptin or 40 μm BAPTA/AM. To measure levels of ASNA1, OPTN, and PERI, cellular lysates (100 μg) were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies that specifically recognize the endogenous protein. D, after normalization to actin in each condition, the relative change in fold intensity of the full-length (for ASNA1 and optineurin) was calculated over the untreated control (value = 1). Changes in fold intensity of total peripherin fragments were determined over the ionomycin-treated sample (value = 1). Each bar represents the mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001. Cont., no treatment; I, ionomycin; C, calpeptin; B, BAPTA/AM.