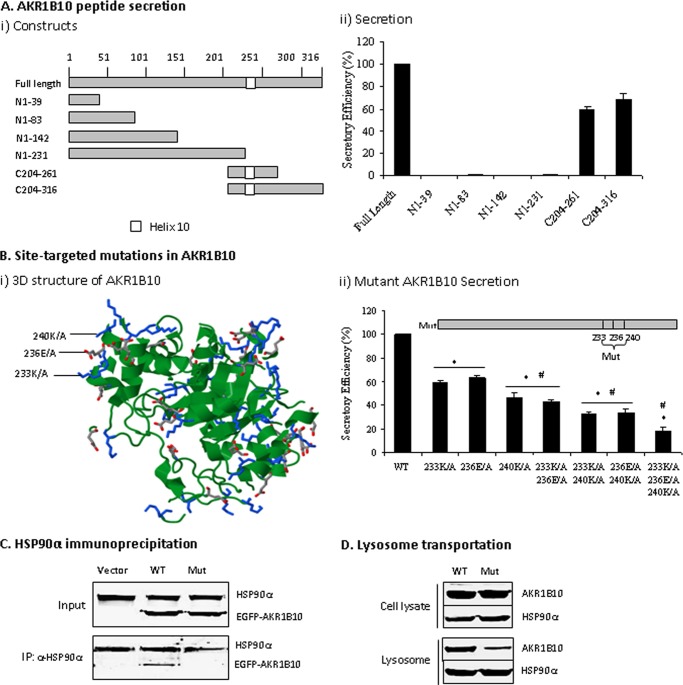
FIGURE 6.
Functional domain mediating AKR1B10 secretion. A, AKR1B10 peptide secretion activity. AKR1B10 full-length (316 aa) and peptide segments, as indicated, were subcloned into a GST-tagged vector (i) and transfected into 293T cells for a secretory activity assay (ii) as described under “Materials and Methods.” Peptide secretory activity was expressed as a percentage of full-length AKR1B10. Data represent the mean ± S.D. from three independent assays. B, site-targeted mutations. i, stereo view of targeted mutation sites in AKR1B10. The image was produced using the Protein Data Bank (see “Materials and Methods”) and shows the position of three targeted mutation sites (Lys-233, Glu-236, and Lys-240) in the AKR1B10 crystal structure. ii, mutational AKR1B10 secretion. Single point mutations (Mut) or combinations, as indicated, were cloned into the CMV/GST-tag vector and transfected into 293T cells for a secretory activity assay as described under “Materials and Methods.” The data indicate the percentage of wild-type AKR1B10. *, p < 0.01 compared with wild-type AKR1B10; #, p < 0.05 compared with the adjacent group on the left. C, HSP90α immunoprecipitation. Wild-type and mutant AKR1B10 (fused with EGFP) with three point mutations were transfected into 293T cells. After 36 h, immunoprecipitation with HSP90α antibody was conducted, and precipitates were subjected to Western blot analysis as described under “Materials and Methods.” D, mutant AKR1B10 in lysosomes. The 293T cells transfected with wild-type or mutant AKR1B10 at three amino acid points were broken by a Dounce homogenizer; lysosomes were isolated from the cells, and HSP90α and AKR1B10 proteins were detected by Western blot analysis.