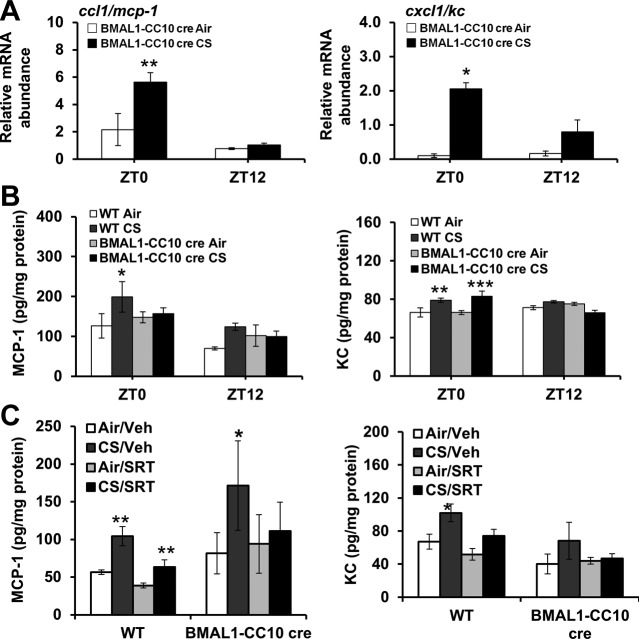
Figure 12.
Lung epithelial cell-specific BMAL1 knockout enhanced CS-induced lung inflammation. A) Expression of proinflammatory cytokine genes (ccl1/mcp-1, and cxcl1/kc) was performed by qPCR. CircWave analysis confirmed circadian rhythms of each proinflammatory cytokine in air-exposed mice. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding air-exposed mice. B) Levels of proinflammatory mediators, including CCL1/MCP-1 and CXCL1/KC, were measured in lung homogenates obtained from air- or CS-exposed WT and BMAL1 CC10 cre mice. Data are shown as means ± se (n=3/group) for each time point. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. corresponding air-exposed mice. C) WT and BMAL1-CC10 cre mice were treated with pharmacologic SIRT1 activator SRT1720 (SRT) or vehicle (Veh) during CS exposure for 3 d. Levels of proinflammatory mediators, such as CCL1/MCP-1 and CXCL1/KC, were measured in lung homogenates obtained from air- or CS-exposed WT and BMAL1-CC10 cre mice. Data are shown as means ± se (n=3 mice/group) for each time point. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. corresponding air-exposed mice.