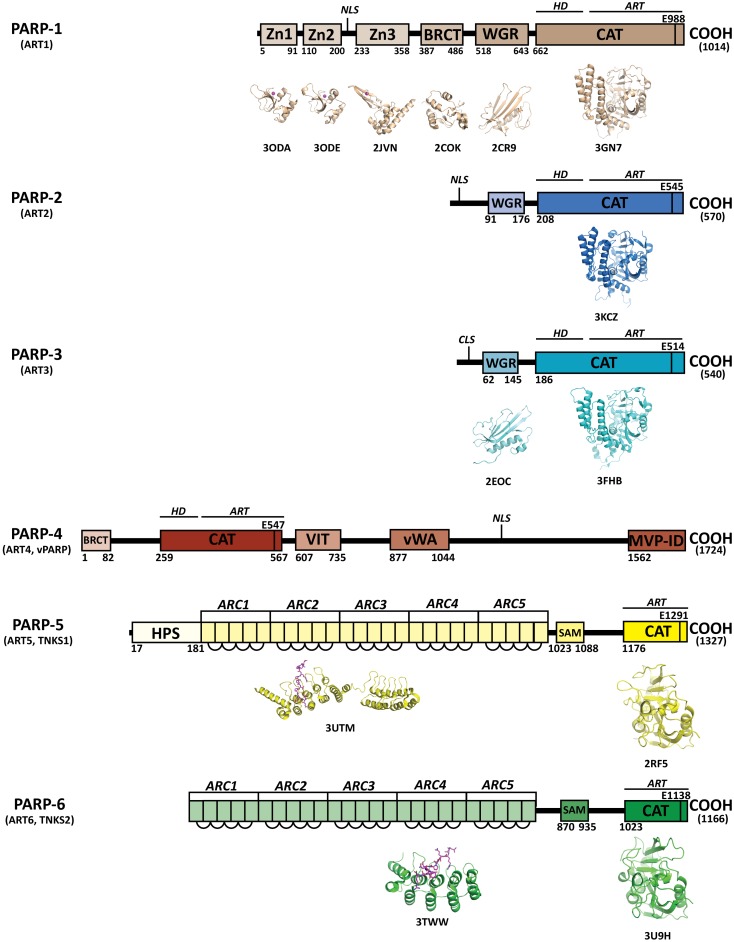
Figure 1.
Domains of human PARPs. A sequence and structural representation of the six bona fide PARPs. Each PARP has a catalytic domain containing an ADP-ribosyltransferase domain (ART) and conserved catalytic glutamic acid residue. In addition PARPs 1–4 contain a helical domain (HD) that serves in allosteric regulation. PARPs 1–3 contain a WGR domain, which is important in DNA-dependent catalytic activation. The breast cancer susceptibility protein-1 C-terminus (BRCT) domain is commonly found in DNA repair and checkpoint proteins, and resides in the automodification domain of PARP-1, and is also present in PARP-4. Zinc-fingers Zn1 and Zn2 of PARP-1 are important in binding DNA, while the third zinc-finger (Zn3) is important in DNA-dependent catalytic activation. Other domains and sequences represented include: centriole-localization signal (CLS), vault protein inter-alpha-trypsin (VIT), von Willebrand type A (vWA), major vault particle interaction domain (MVP-ID), His-Pro-Ser region (HPS), ankyrin repeat clusters (ARCs), sterile alpha motif (SAM), and nuclear localization signal (NLS).