Fig. 6.
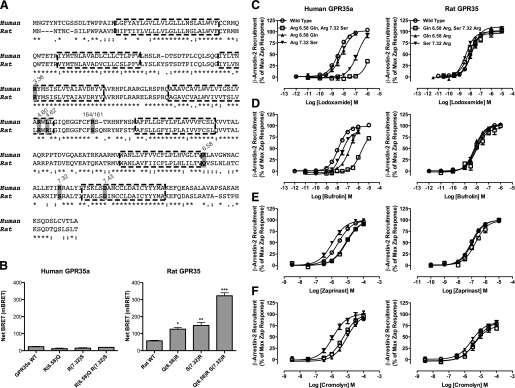
Swapping nonconserved arginine residues between human and rat GPR35a influences ligand potency. (A) Alignment of the sequences of human GPR35a and rat GPR35. Key residues that vary between the two orthologs that were swapped between species or otherwise modified are highlighted, as are the conserved arginine at position 3.36 that acts as a key ligand binding contact in both species and the aspartate at position 7.43, predicted to form an ionic interaction with arginine 3.36 in the absence of agonist. (B) Mutations altered the basal, ligand-independent activity at rat GPR35 but not at human GPR35a. Significantly different from wild type at *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. The ability of lodoxamide (C), bufrolin (D), zaprinast (E), and cromolyn disodium (F) to promote interactions between human GPR35a (left side) and rat GPR35 (right side) with β-arrestin-2 are shown for wild-type (WT) and ortholog residue swaps at positions 6.58, 7.32, and 6.58 plus 7.32.
