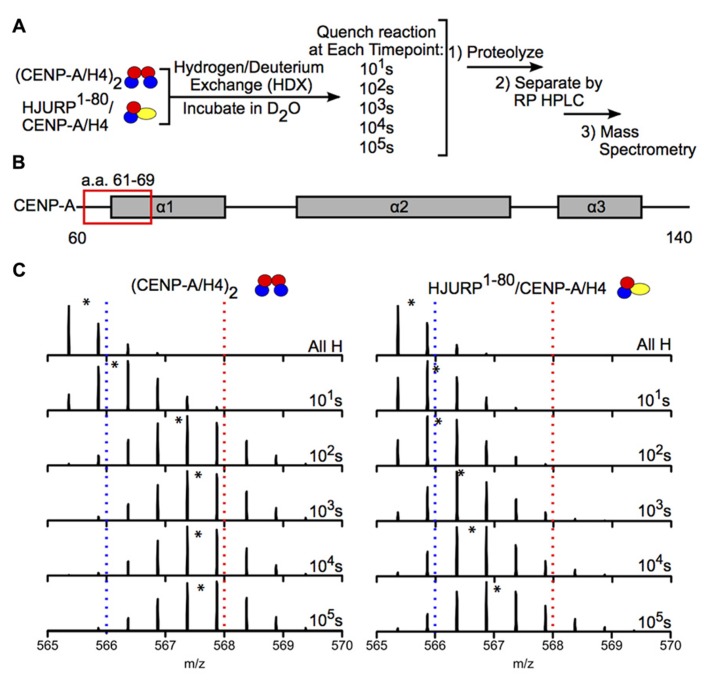
FIGURE 6.
Hydrogen-deuterium exchange reveals increased stability in CENP-A/H4 dimers bound to HJURP relative to (CENP-A/H4)2. (A) Schematic of experimental setup for HDX experiment. CENP-A/H4 bound to HJURP and (CENP-A/H4)2 were incubated in D2O to allow for backbone amide exchange. Reactions were quenched after the indicated time points. The protein complexes were proteolyzed, separated via RP-HPLC and analyzed via MS. (B) Schematic of CENP-A secondary structural features. The red box indicates the location of a peptide spanning residues 61–69. (C) Side-by-side analysis of raw data for CENP-A peptide 61–69 from (CENP-A/H4)2 (left) and HJURP1-80/CENP-A/H4 (right). Black asterisks denote centroid locations, and dotted red and blue lines serve as guideposts to highlight the differences in m/z shifts between the two complexes. Note that the CENP-A peptide is more protected from exchange in the HJURP1-80/CENP-A/H4 complex compared to the heterotetramer as evidenced by a lower level of deuterium incorporation throughout the time course, where it takes >100 times as long to achieve the same level of HDX. Data obtained from Bassett et al. (2012).