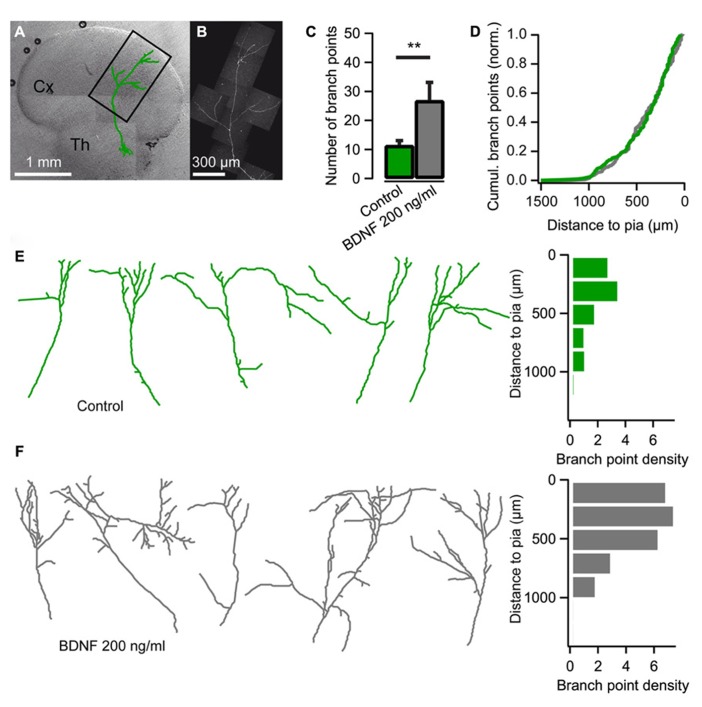
FIGURE 1.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes axon branching in thalamocortical co-cultures. (A) Reconstruction of a thalamic neuron expressing EYFP (green) superimposed on a differential interference contrast-enhanced micrograph of a thalamocortical co-culture. Cx cerebral cortex; Th thalamus. (B) Confocal micrograph of the axon from the neuron reconstructed in A. (C) Bar diagram for the average number of axonal branch points (the number of times the axon bifurcates) when BDNF is added to the medium. The error bars represent SEM. **P < 0.01. (D) Cumulative plot of branch-point location with respect to pial surface for control cultures (green) and cultures treated with BDNF (gray). (E) Reconstructions of representative axons from thalamic cells in the neocortical explant and a histogram showing the distribution of axonal branch points with respect to the pial surface. Branch-point density = number of branch points/number of axons. (F) Reconstructions of representative axons from thalamic cells in the neocortical explant when BDNF was added to the medium. A histogram plotting the distribution of the axonal branch points with respect to the pial surface is shown on the right.