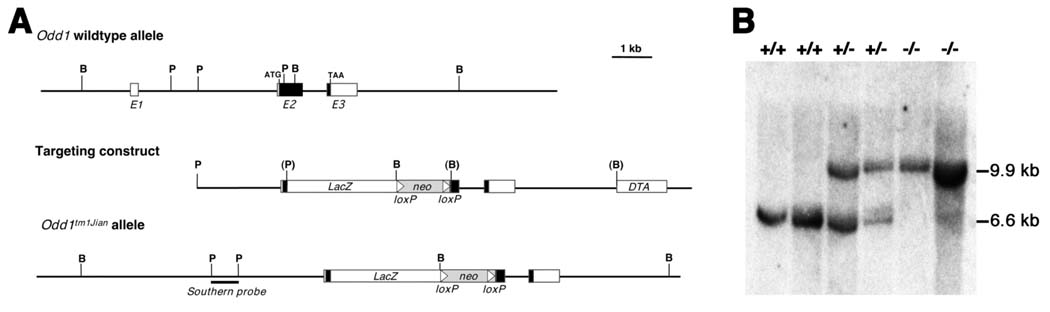
Fig. 1.
Targeted disruption of the mouse Odd1 gene. (A) The Odd1 gene consists of three exons spanning approximately 6 kb of genomic DNA. Boxes indicate exons, with the protein-coding region marked in black. The positions of the translation start (ATG) and stop (TAA) codons are also indicated. Restriction sites are: B, BamHI; P, PstI. The targeting vector used the 2.1 kb PstI fragment containing the intron 1/exon 2 junction as the 5’ arm and the 5.3 kb BamHI fragment located 335 bp downstream as the 3’ arm. A modified bacterial lacZ gene and a loxP-flanked neo expression cassette were inserted in between the arms and a diptheria toxin A (DTA) expression cassette was cloned 3’ to the 3’ arm for negative selection against random integration. (B) Southern hybridization analysis of E11.5 embryonic DNA samples from a litter of F1 heterozygous intercross. The genomic DNA samples were digested with BamHI, separated by electrophoresis through a 0.8% agarose gel, transferred onto a Zetaprobe nylon memberane (BioRad), and hybridized with random prime-labeled probes made from the 700 bp PstI fragment isolated from the Odd1 genomic region 5’ to the targeted region. The 6.6 kb BamHI fragment corresponding to the wildtype allele was detected in wildtype and heterozygous embryos, while the 9.9 kb mutant allele-specific fragment was only detected in heterozygous and homozygous mutants. +/+, wildtype; +/−, heterozygous; −/−, homozygous mutant.