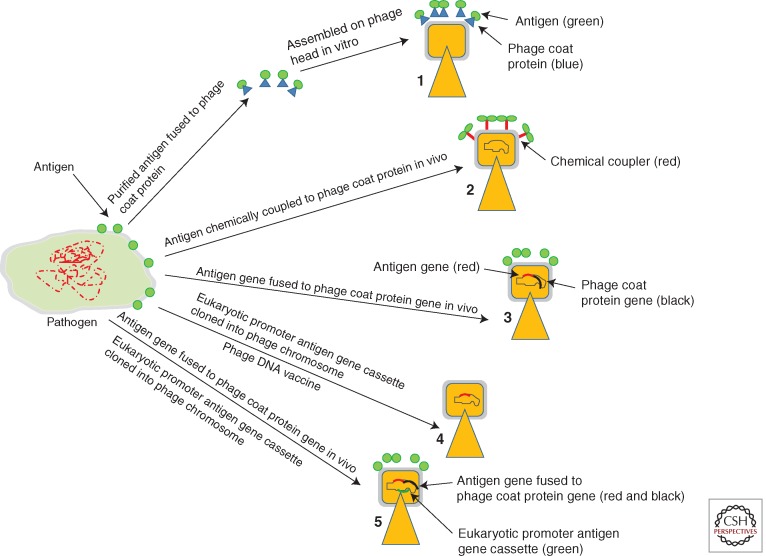
Figure 2.
Schematic representations of several phage-mediated vaccine delivery systems. (1) Production of virus-like particles (VLPs) by adding purified phage capsid proteins fused to antigens during assembly of phage particles in vitro. (2) Antigens are attached by chemical conjugation on preassembled phage head. (3) Antigens are displayed on phage surface by fusion of antigen genes with phage capsid protein genes. (4) Phage as a DNA delivery vehicle where antigen genes are cloned in phage genome under the control of eukaryotic promoters. (5) Phage for DNA vaccine, where phage carries antigen genes under the control of eukaryotic promoters. The phage also displays foreign proteins on its surface as fusion of phage capsid proteins. This protein targets the phage to antigen-presenting cells (APC).